Milling is a crucial manufacturing process involving removing material from a workpiece using rotary cutters. With advancements in technology, milling has evolved from manual methods to computer-controlled processes, with the introduction of CNC (Computer Numerical Control) milling.
While manual milling has been the traditional approach for centuries, CNC milling has gained popularity recently due to its increased precision, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. However, this has sparked a debate among manufacturers about which method is superior – manual or CNC. We will delve into the differences between manual milling and CNC milling techniques, their advantages, and limitations to provide a comprehensive understanding of manual and CNC milling.

Definition And Feature Of Manual Milling
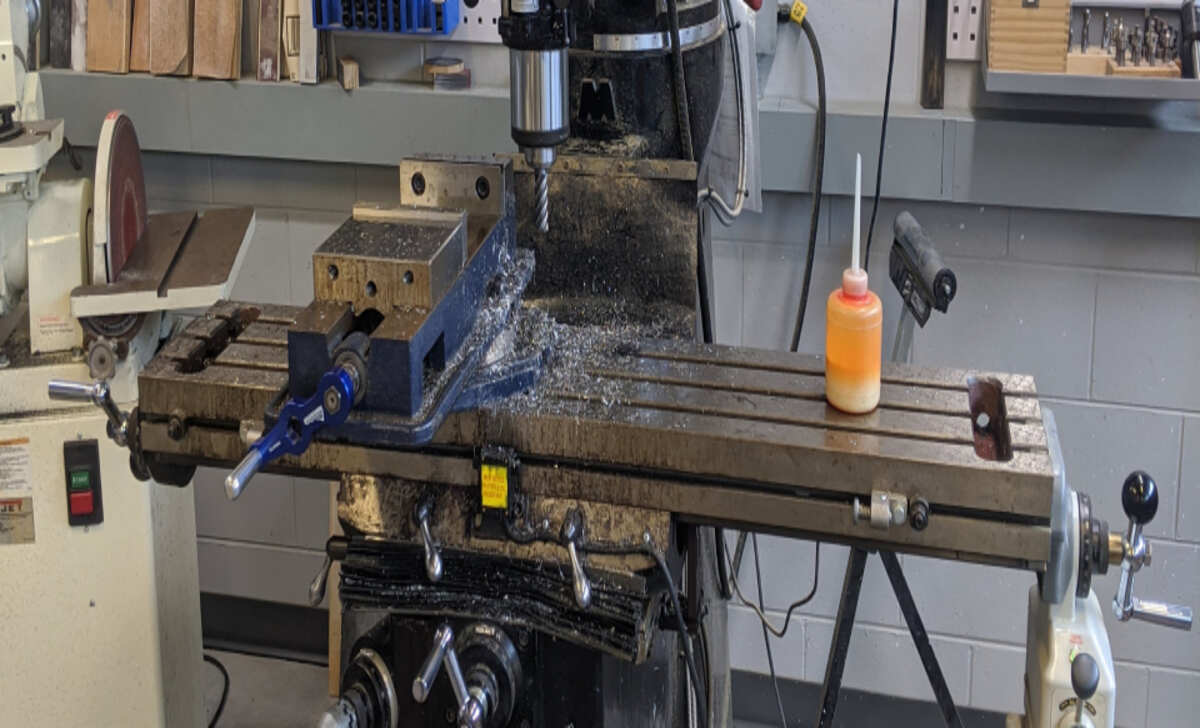

Manual milling is a machining process involving using a machine to remove material from a workpiece. Its hands-on approach requires the operator to manually control the movement of the cutting tool and the workpiece. Manual milling allows for precision and versatility, allowing users to create intricate shapes and designs. It is commonly handy in smallscale production, prototyping, and repair work. The operator’s skill and experience are crucial in achieving accurate and high-quality results.
Specification
- Machine Type: Manual Milling Machine
- Operation: Manual control
- Spindle Speed: Adjustable
- Spindle Taper: R8 or NT30
- Table Size: Varies
- XAxis Travel: Varies
- YAxis Travel: Varies
- ZAxis Travel: Varies
- Power Feed: Optional (X and Y axes)
- Quill Travel: Varies
- Spindle Motor: Varies
- Weight: Varies
Pros
- Allows for precise control over the milling process
- Enhances operator skill and craftsmanship
- It can be more cost-effective for smallscale operations
- Provides flexibility to adapt to different materials and projects
cons
- Requires more time and effort compared
Definition And Features Of Cnc Milling
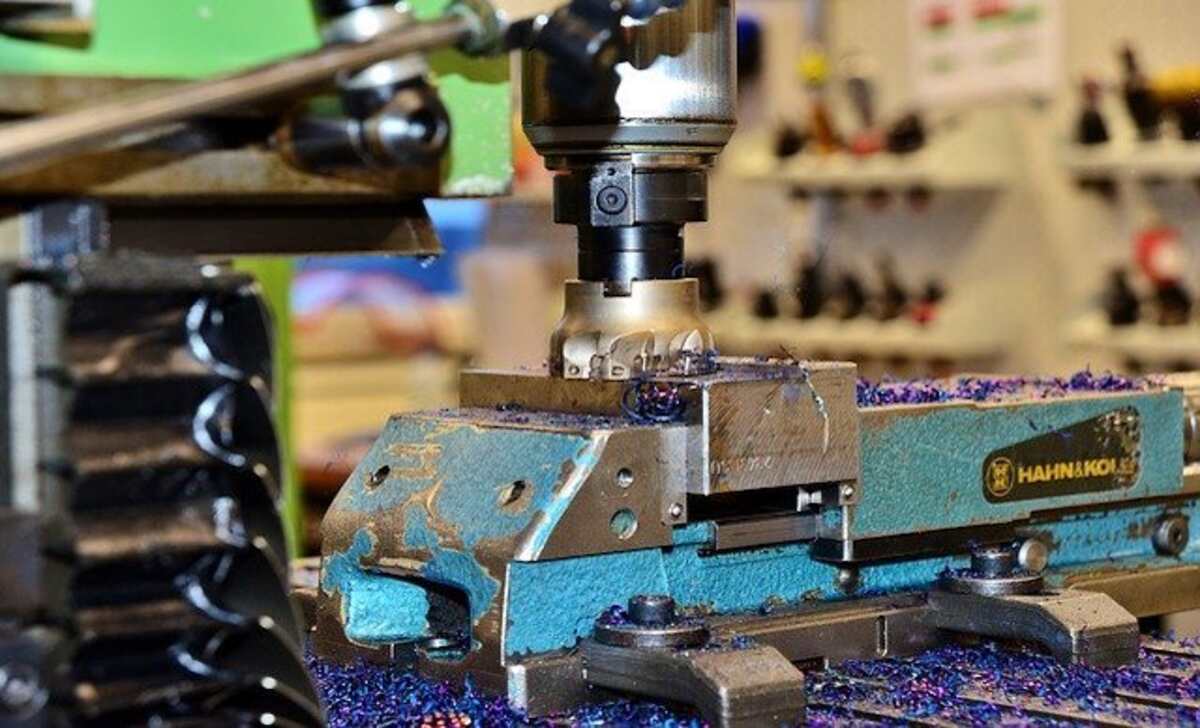
CNC milling, an abbreviation for Computer Numerical Control milling, is a sophisticated machining process that utilizes computerized controls to remove material from a workpiece precisely. It offers numerous features, including high precision, repeatability, and the ability to create complex shapes. CNC milling machines use rotating cutting tools to carve out parts and components with incredible accuracy, making them a popular choice in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing.
Specification
- Axis: 3, 4, or 5 axis
- Workpiece Dimensions: Varies based on machine capabilities
- Spindle Speed: Adjustable range, typically in RPM
- Feed Rate: Adjustable range, typically in IPM
- Accuracy: High precision, typically within microns
- Tooling: Various tool holders and cutting tools
- Control System: CNC controller with programming interface
- Software: CAM software for generating tool paths
- Material Compatibility: A wide range of materials can be milled
- Workholding: Vises, clamps, or custom fixtures
Pros
- Precision: CNC milling allows
- Efficiency: CNC milling machines can work continuously
- Versatility: CNC milling can be handy on a wide range
- Automation: CNC milling machines are automated
cons
- Cost: CNC milling machines can be expensive
Comparison Between Manual Milling Vs CNC Milling
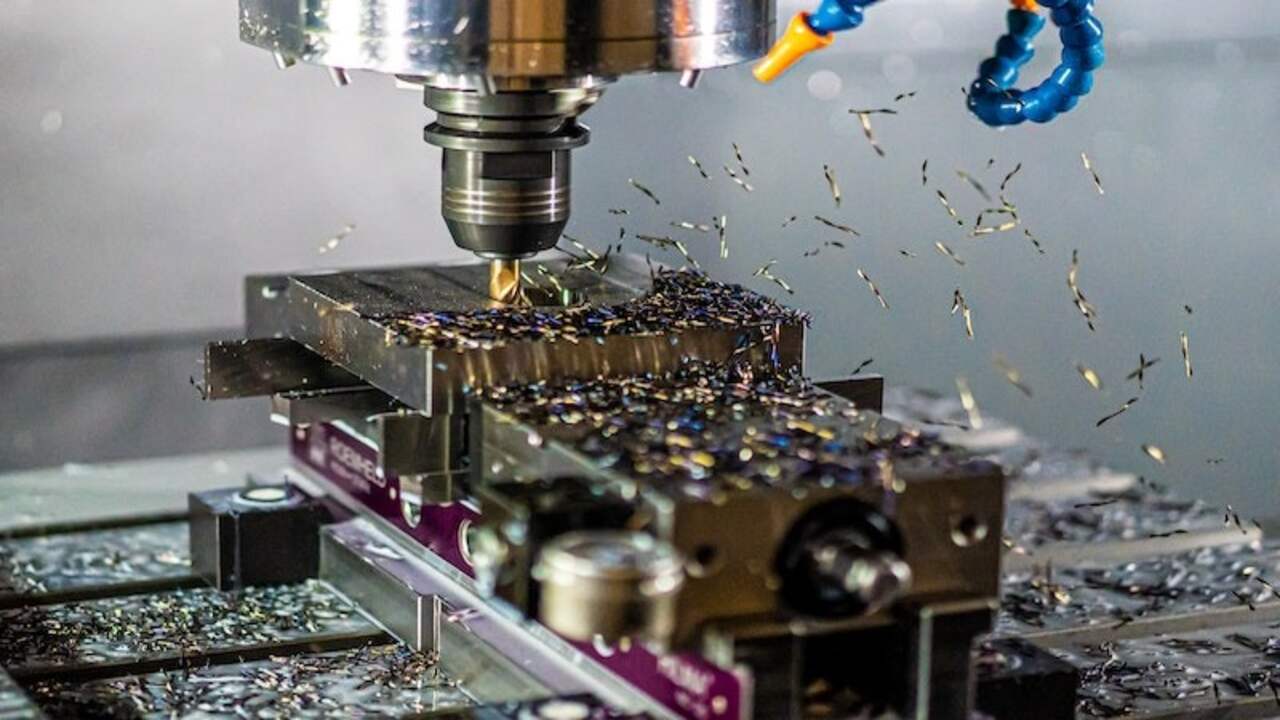

CNC milling offers enhanced efficiency and productivity compared to manual milling. CNC milling allows for easy execution of precise and complex designs, resulting in higher accuracy and faster production times.
On the other hand, manual milling requires skilled operators who can manually operate the machine and may be limited in precision and speed. Understanding this distinction allows businesses to decide which method to employ based on their needs and goals. Below, we discuss the differences between manual milling and CNC milling.
1. Accuracy And Precision
Regarding accuracy and precision, there is a noticeable difference between manual milling and CNC milling. Manual milling requires the operator to manually control the movement of the milling machine, which can result in slight variations and inconsistencies.
On the other hand, CNC milling utilizes computer-controlled movements, ensuring consistent and precise results. This level of precision is especially crucial in industries that require tight tolerances and intricate designs. CNC milling offers enhanced accuracy and efficiency, making it the preferred choice for many manufacturing processes.
2. Speed And Efficiency
Manual milling and CNC milling are two methods that are handy in machining. Manual milling involves using a manual milling machine, where the operator controls the movement of the cutting tool. On the other hand, CNC milling utilizes computer numerical control to automate the milling process.
This allows for greater precision, repeatability, and faster production times than manual milling. While manual milling requires skilled operators, CNC milling offers increased speed and efficiency, making it a preferred choice for many industries.
3. Complexity And Programming Requirements
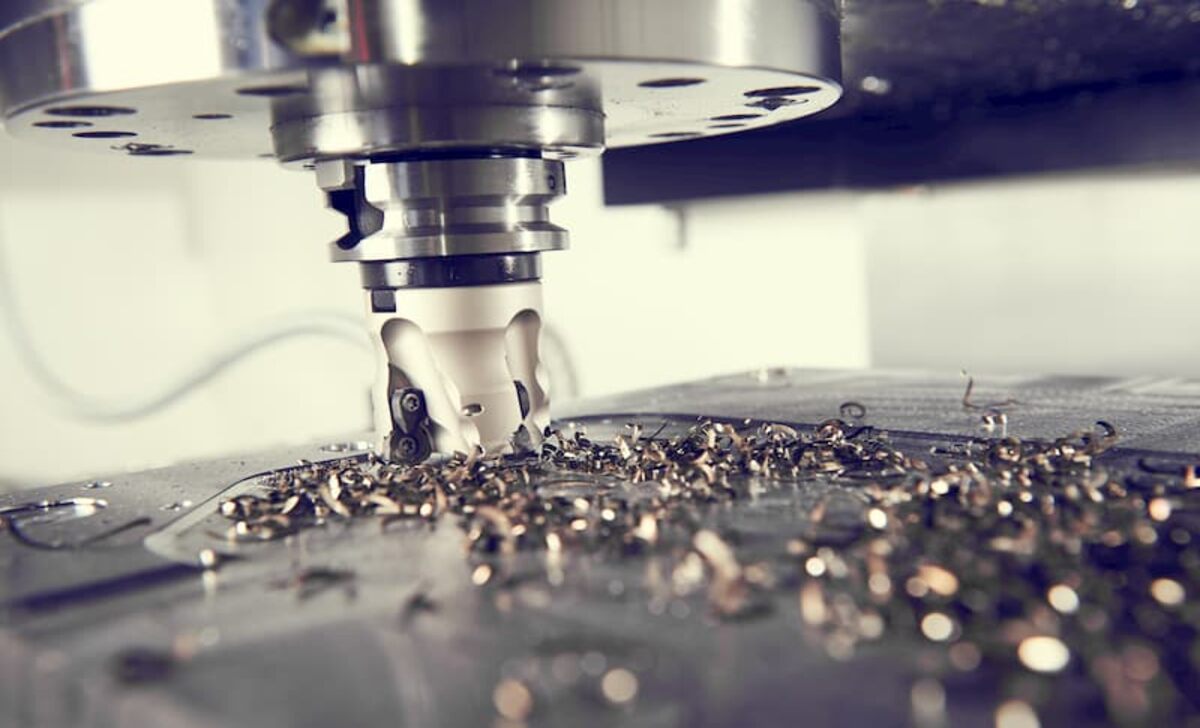

Regarding milling machines, there are two main options to consider: manual milling machines and CNC machines. Manual milling machines require the expertise of a skilled manual machinist who can operate the machine by hand, adjust settings, and make precise cuts.
On the other hand, CNC machines use computer programming to automate the milling process, increasing efficiency and accuracy. While manual machining allows for more flexibility and customization, CNC milling offers higher precision and faster production rates. Ultimately, the choice between manual and CNC milling depends on the complexity of the project and programming requirements.
4. Flexibility And Versatility
In the machining business, flexibility and versatility are crucial factors when comparing manual and CNC milling. While manual milling requires skilled operators to control the machine’s movements manually, CNC milling offers enhanced precision and automation.
The CNC Max Tabletop Mill is a prime example of this, as it combines the power of computer programming with advanced milling capabilities. With CNC milling, businesses can achieve higher accuracy, faster production, and increased efficiency, making it an ideal choice for those seeking innovation in the machining industry.
5. Cost Considerations
Regarding cost considerations, comparing manual milling with CNC milling is crucial. CNC capability offers numerous advantages, including increased precision, efficiency, and consistency. By utilizing CNC machining, manufacturers can reduce the need for manual labour, resulting in cost savings.
Additionally, CNC milling machines easily produce complex and intricate designs, enhancing productivity and reducing production costs. Therefore, it is evident that CNC machining provides a cost-effective solution for milling processes.
Factors To Consider When Choosing Between Manual Milling And Cnc Milling

When deciding between manual milling and CNC milling, several factors must be considered. One important factor is the CNC capability. CNC machining offers precise and efficient operations, allowing for complex designs and intricate details. On the other hand, manual milling requires skilled operators and can be time-consuming for intricate tasks.
Additionally, CNC milling offers increased productivity and repeatability, making it ideal for large-scale production. Ultimately, the choice between manual and CNC milling depends on the specific requirements of the project and the desired level of precision and efficiency.
1. Type Of Project Or Application
When deciding between manual and CNC milling for your project or application, there are several factors to consider. Manual milling offers the advantage of being more cost-effective and flexible for smallscale projects, allowing for greater manual control and customization. On the other hand, CNC milling provides higher precision, efficiency, and consistency for larger-scale projects, reducing the risk of human error. Additionally, CNC milling offers the ability to automate processes and easily handle complex designs.
2. Time Constraints
Manual milling requires skilled operators who may take longer to complete tasks than CNC milling, which is automated and operates faster. However, it is important to weigh the benefits of precision and flexibility that manual milling offers against the efficiency and speed of CNC milling. The project’s complexity, available resources, and budget should also be considered when deciding. Finding the right balance between these factors is essential to ensure the successful execution of milling operations.
3. Required Level Of Accuracy

Regarding choosing between manual milling and CNC milling, several factors must be considered to ensure the desired level of accuracy. One crucial aspect to consider is the operators’ expertise and skill level. With manual milling, the accuracy of the final product heavily relies on the proficiency of the individual operating the machine.
On the other hand, computer programming controls CNC milling, offering higher precision and reducing the margin of error caused by human intervention. Additionally, you should consider the complexity of the project. For simple milling tasks, manual milling may be sufficient.
Applications And Industries
Manual milling is commonly handy in woodworking, metalworking, and prototyping industries. Its versatility allows for intricate customization and adjustments. On the other hand, CNC milling is prevalent in aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing industries, where precision and high-volume production are essential.
Specific applications for manual milling include creating unique furniture pieces or designing intricate metal components, while CNC milling excels in producing complex parts, moulds, and precise components for mass production.
Case Studies And Examples
Regarding manual milling versus CNC milling, real-life examples can provide valuable insights. For instance, manual milling may be preferred in a smallscale production setting due to its lower upfront costs and simplicity.
On the other hand, in large-scale manufacturing, CNC milling offers higher precision and efficiency. The benefits and outcomes of choosing either method depend on the specific scenario, such as the required production volume, complexity of the part, and available resources.
Conclusion
Both manual milling and CNC milling have their advantages and disadvantages. While manual milling allows for a more hands-on and precise approach, CNC milling offers greater automation and efficiency. Manual milling allows for a more traditional and hands-on approach, which can result in higher precision.
On the other hand, CNC milling offers greater automation and efficiency, making it a popular choice for high-volume and complex projects. Ultimately, the choice between the two will depend on the specific needs and capabilities of the project. As technology advances, manufacturing industry professionals need to stay informed and adaptable to utilize the best techniques for their projects.
FAQs
1.Is CNC Faster Than Manual?
Ans: CNC (Computer Numerical Control) is generally faster than manual machining. This is because CNC machines are controlled by computer programs, which allow for precise and automated movements of the machine tools.
2.Why Use CNC Milling?
Ans: CNC milling is handy for its precision, efficiency, and versatility in creating complex and detailed parts. It allows for producing highly accurate and consistent components, reducing the risk of errors and ensuring quality.
3.Are Manual Mills Still Used?
Ans: Yes, manual mills are still used in various industries and settings. While automated mills and machinery have become more prevalent, manual mills are valued for their versatility, simplicity, and cost-effectiveness.
4.What Is A Manual Mill Used For?
Ans: A manual mill is used for various purposes, such as grinding, crushing, or cutting materials. It typically consists of a rotating mechanism, such as a hand crank or wheel, and a grinding surface or cutting blades.
5.Is CNC More Expensive?
Ans: CNC (Computer Numerical Control) technology can be more expensive initially due to the cost of the machinery and software. However, CNC can be more cost-effective in the long run compared to traditional manufacturing methods.







