Milling machines are essential in manufacturing and engineering, allowing for precise and efficient shaping of various materials. These versatile machines are handy for various applications, from creating intricate parts for machinery to producing custom pieces for specific projects.
However, milling machines require various components, including the drawbar, to operate at their full potential. The drawbar is a critical part of the milling machine that plays a significant role in securing the tooling and ensuring the accuracy and stability of the machine’s cutting process.
Here, we will delve into the world of milling machine drawbars, exploring their purpose, types, and maintenance tips. Whether you are a seasoned machinist or a beginner, will provide valuable insights into this essential component of milling machines.

Milling Machine Drawbar – Explain In Detail
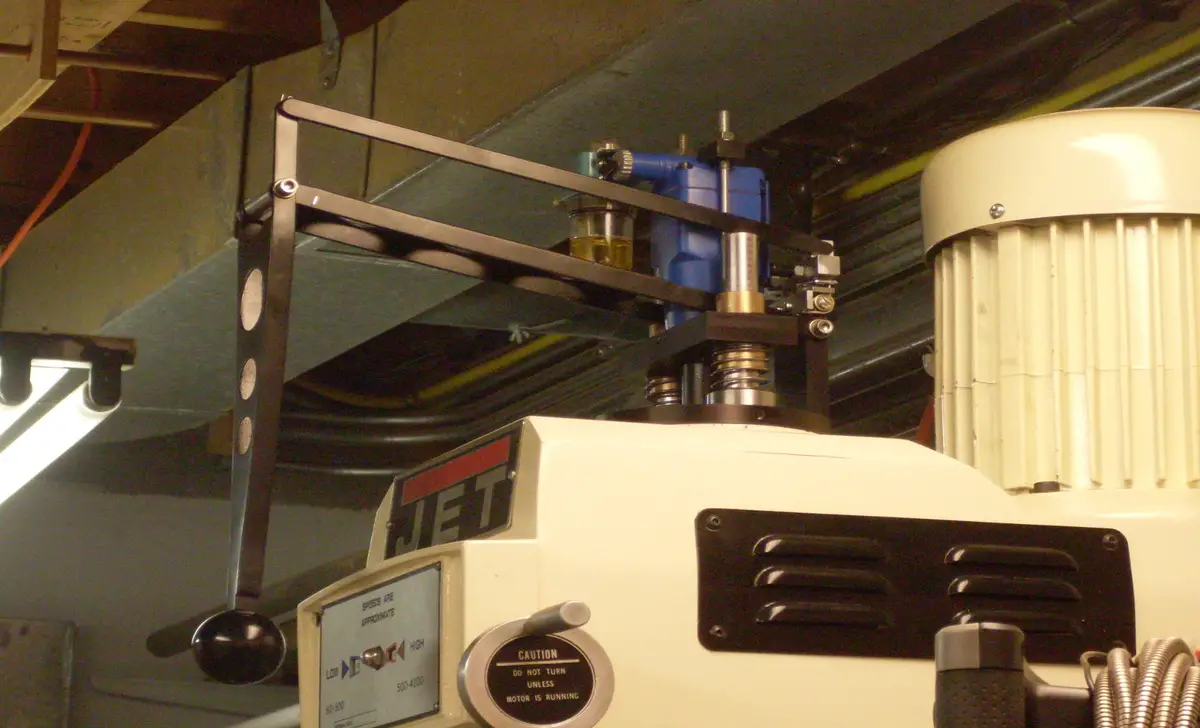
A drawbar on a milling machine is handy to secure the tooling or cutting tool in place. It is typically a threaded rod that connects the milling machine’s spindle to the tool holder or collet. Depending on the machine, the drawbar is tightened or loosened using a wrench or a special drawbar wrench.
This allows for a secure and tight connection between the spindle and the tool, ensuring accurate and precise machining operations. The drawbar is essential in milling machines as it helps maintain stability and rigidity during the milling process.
The Role Of A Drawbar In Milling Operations

In milling operations, the drawbar is crucial in ensuring the tool’s secure retention within the spindle. It acts as a retention system, holding the tool holder in place during cutting. By applying clamping force, the drawbar prevents slippage or movement, ensuring stable and precise machining.
Proper drawbar function is essential for maintaining spindle alignment, preventing tool damage, and achieving accurate and repeatable milling results. Ultimately, the drawbar’s role is vital in maintaining safety, efficiency, and precision in milling operations.
Key Components Of A Drawbar
The drawbar assembly consists of several key components that secure the tool holder within the spindle and apply the necessary clamping force. These components include the spindle drawbar, drawbar collet, and drawbar spring. The spindle drawbar is a threaded rod that extends through the spindle and holds the tool holder in place.
The drawbar collet accommodates various tool holder sizes and types, providing versatility in milling applications. The drawbar spring ensures consistent tension and the proper clamping force for different milling operations. Understanding these components’ design and function is crucial for efficient milling machine operation.
Types Of Milling Machine Drawbars

Various drawbars are available for milling machines, each offering unique advantages and functionality. A milling machine drawbar is an integral component of a milling machine tool, responsible for securing various cutting tools and accessories in place during the machining process.
This vital mechanism allows for the precise positioning and alignment of the tools, ensuring accurate and efficient milling operations. The drawbar acts as a clamping device, holding the tool firmly in position while the machine’s spindle rotates at high speeds, enabling the cutting action. Some common types include mechanical drawbars, hydraulic drawbars, and pneumatic drawbars. Let’s explore each type.
Mechanical Drawbars
Mechanical drawbars utilize manual or power-operated mechanisms to apply clamping force to the tool holder. They are popular for their reliability, simplicity, and ease of maintenance, making them a popular choice for conventional milling machines. Mechanical drawbars offer precise control over clamping force, suitable for various milling operations. The features and benefits of mechanical drawbars make them an ideal solution for tool retention, ensuring accurate and repeatable machining results.
Hydraulic Drawbars

Hydraulic drawbars utilize hydraulic pressure to apply uniform and powerful clamping force, securing the tool holder. These drawbars offer rapid tool changes, high clamping forces, and enhanced precision, making them ideal for advanced milling applications. Hydraulic drawbars contribute to increased productivity, tooling flexibility, and reduced setup times, improving milling machine performance in demanding operations.
Pneumatic Drawbars
Pneumatic drawbars utilize compressed air to generate clamping force, providing quick and efficient tool change capabilities. These drawbars offer fast release and secure tool clamping, making them suitable for rapid production environments. Pneumatic drawbars improve spindle utilization, minimize downtime, and increase milling efficiency. Their operational principles and advantages make them a valuable tool in manufacturing facilities requiring high throughput and consistent milling performance.
How Does A CNC Drawbar Work?

CNC drawbars are a specific type of drawbar designed for computer numerical control (CNC) milling machines. These drawbars automate the tool change process, optimizing efficiency and reducing human error. The operation procedure of a CNC drawbar involves automated tool change sequences, spindle engagement, and clamping force adjustments.
It follows programmed instructions to synchronize tool exchange with spindle positioning and cutting operations. CNC drawbars integrate with the control unit, ensuring reliable, repeatable, and precise tool handling during milling operations.
Operation Procedure Of A CNC Drawbar
The operation of a CNC drawbar involves automated tool change sequences, spindle engagement, and clamping force adjustments. It follows programmed instructions to synchronize tool exchange with spindle positioning and cutting operations.
The CNC drawbar’s operation procedure aims to minimize downtime, optimize tool utilization, and enhance machining productivity. It integrates with the CNC control unit to ensure reliable, repeatable, and precise tool handling during milling operations. Understanding the operational sequence and functionalities of a CNC drawbar is essential for maximizing CNC milling efficiency.
CNC Drawbar Vs Traditional Drawbars
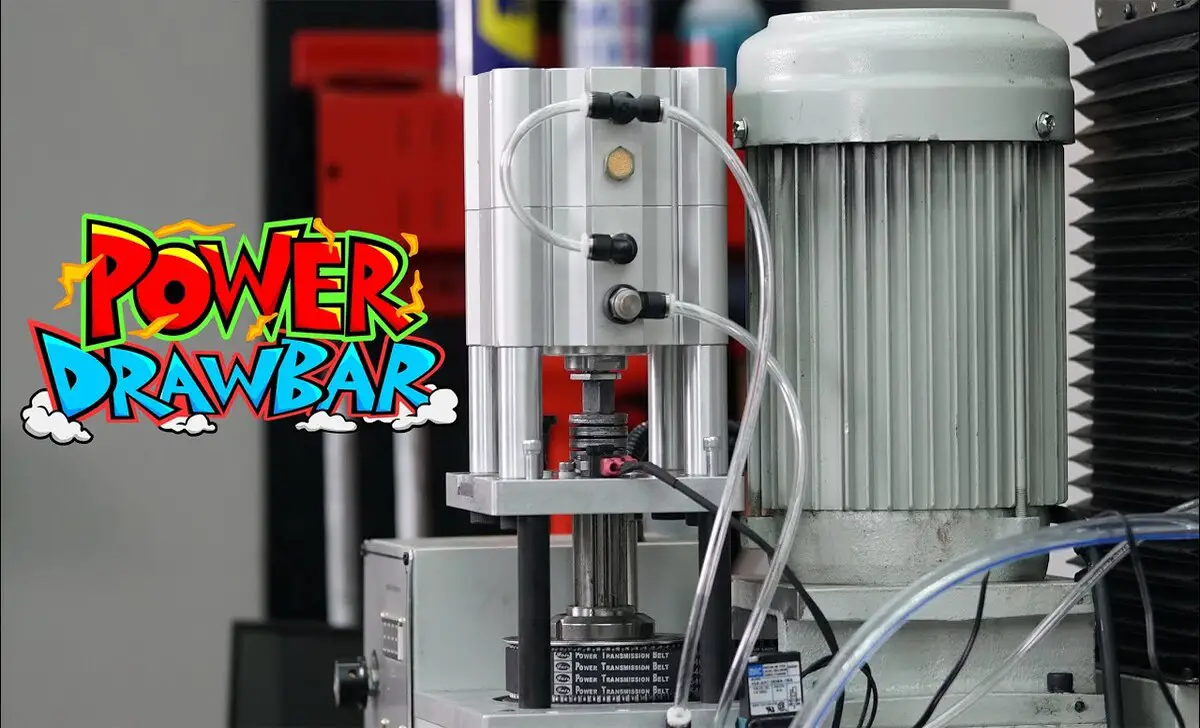
CNC drawbars offer automated tool change capabilities, precise clamping force control, and seamless integration with CNC machining processes. They prioritize efficiency, accuracy, and flexibility, catering to the demands of modern CNC milling operations.
On the other hand, traditional drawbars rely on manual or power-operated mechanisms, making them suitable for conventional milling machines and specific machining applications. Understanding the distinctions between CNC and traditional drawbars is essential for selecting the most suitable option based on milling machine requirements.
Maintenance Tips For Milling Machine Drawbars
Drawbars typically consist of a threaded rod or shaft connected to the milling machine’s spindle through components such as nuts and washers. This threaded rod creates the necessary tension to secure the cutting tool or accessory firmly. By tightening or loosening the drawbar, operators can quickly and easily change tools, allowing for a seamless transition between machining operations. Here are Maintenance Tips for Milling Machine Drawbars:
- Regularly inspect the drawbar for any signs of wear or damage
- Clean the drawbar and surrounding area to remove dirt and debris
- Lubricate the drawbar with a suitable lubricant to ensure smooth operation
- Check the drawbar tension regularly and adjust it if necessary
- Replace worn or damaged drawbars promptly to prevent further damage to the milling machine
- Keep the drawbar area free from chips and other materials that may interfere with its operation
Common Issues With Milling Machine Drawbars
The design and construction of milling machine drawbars vary depending on the specific model and manufacturer. However, they all aim to provide a reliable and secure clamping mechanism. Drawbars typically come from high-quality materials such as hardened steel or alloy steel to ensure durability and resistance to wear and tear.
Regular maintenance and inspection of milling machine drawbars are essential to ensure optimal performance and safety. Any wear, damage, or improper functioning signs should be addressed promptly to prevent accidents and machine downtime. Here are Common Issues with Milling Machine Drawbars:
- Drawbar jamming or getting stuck
- The drawbar is not properly aligned with the collet or tool holder
- Insufficient drawbar tension, causing tool slippage
- Drawbar threads becoming worn or damaged
- The drawbar is not properly lubricated, leading to increased friction and wear
- The drawbar is not securely tightened, resulting in tool chatter or vibrations.
Tips And Best Practices For Using Drawbars On A Milling Machine

One crucial component of these machines is the drawbar. The drawbar connects the milling machine’s spindle and the tool holder, ensuring a secure and rigid grip during operation. The primary purpose of a milling machine drawbar is to provide the necessary force to hold the tool securely in place.
It usually comes with high-strength steel to withstand the forces generated during machining. The drawbar is threaded on one end to screw into the spindle, while the other end is designed to accommodate different types of tool holders, such as collets or end mill holders. Here are Tips and Best Practices for Using Drawbars on a Milling Machine:
- Familiarize yourself with the drawbar mechanism on your specific milling machine.
- Ensure that the drawbar is securely tightened before operating the machine.
- When handling the drawbar, use proper safety equipment, such as gloves and safety glasses.
- Regularly clean and inspect the drawbar for any signs of wear or damage.
- Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for lubrication and maintenance of the drawbar.
- Avoid overloading the drawbar with excessive force or weight.
- Use the appropriate tools and techniques when releasing or tightening the drawbar.
- Always operate the milling machine within its specified weight and capacity limits.
Conclusion
Milling machine drawbars are crucial in ensuring smooth and efficient milling operations. Understanding the basics of drawbars, including their components and types, is essential for selecting the right one for your needs. Whether you opt for mechanical, hydraulic, or pneumatic drawbars, each has advantages and considerations.
It is important for those working with CNC machines to understand how CNC drawbars work and their differences from traditional drawbar safety. Regular maintenance of milling machine drawbars is vital to prolong their lifespan and prevent common issues. Following proper operation procedures and promptly addressing problems can ensure optimal performance and avoid costly downtime.
Frequently Asked Questions
1.How Does A Drawbar Work?
A drawbar is crucial in securing a milling machine’s collets or tool holders. It passes through the spindle and tightly grips the tool by threading it into the collet.
2.How Does A Spindle Drawbar Work?
A spindle drawbar secures the cutting tool or workpiece on a milling machine. It is inserted into the spindle and tightened, applying pressure to hold onto the tool or workpiece. To release, the drawbar is loosened and removed from the spindle.
3.What Is The Function Of The Draw Bolt On The Milling Machine?
The function of a draw bolt on a milling machine is to secure tool holders or collets onto the spindle. It pulls the tool holder or collet into the spindle taper, creating a tight fit.
4.What Is A CNC Drawbar?
A CNC drawbar dynamometer is an automated device found in milling machines that securely hold the tool. It replaces manual drawbar components and allows for faster and safer tool changes.
5.How Do You Use A Milling Machine?
Start by securing the workpiece to the table using a milling machine. Then, insert the appropriate cutting tool into the spindle and adjust the depth and speed. Finally, carefully move the tool across the workpiece to create the desired shape or cut.