Regarding milling, various types of machines can be used to produce precision parts and components. Knee mills and bed mills are two popular options among these machines. Both of these machines have their unique features and advantages, but which one is the better choice?
We will delve into the differences between Knee Mill vs Bed Mill and discuss their pros and cons. By understanding each machine’s distinct characteristics and capabilities, readers will better understand which suits their specific needs. So, let’s dive in and explore the nuances of knee and bed mills and discover which one reigns supreme in the machining world.
Definition And Features Of Knee Mill
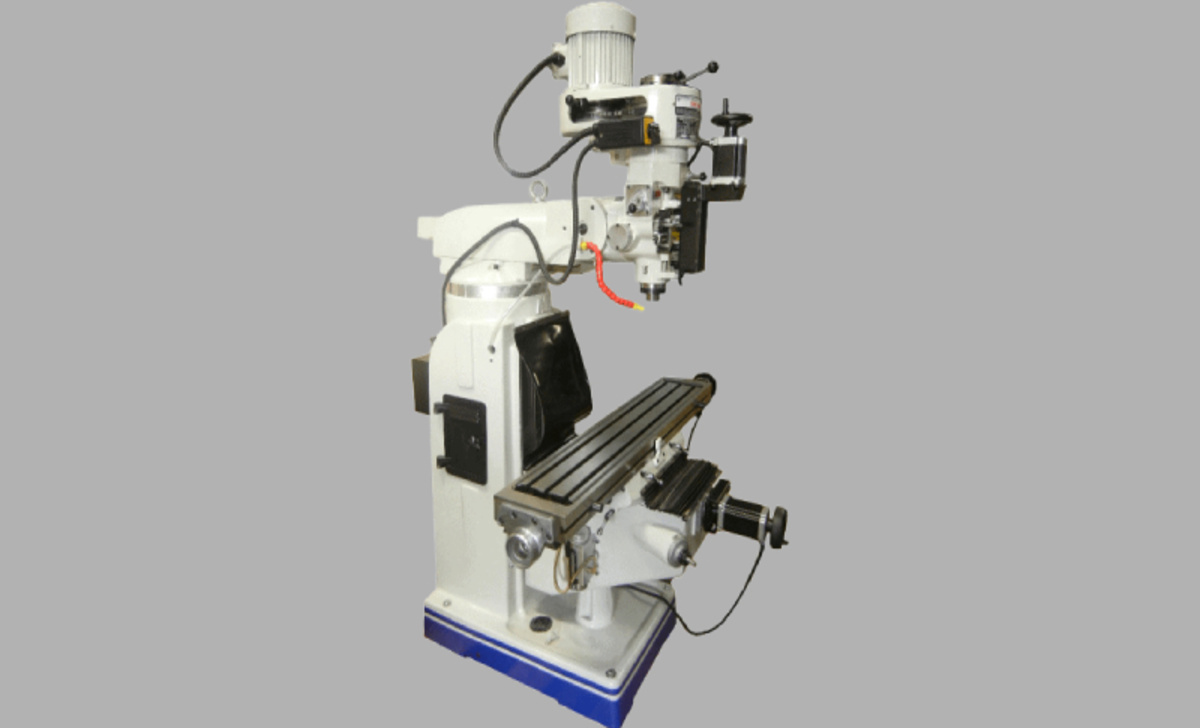

A knee mill, also known as a vertical milling machine, is a type of milling machine that has a vertically adjustable worktable resting on a saddle that is supported by a knee. This machine is widely used in machining operations and offers various features such as precise adjustments, versatile cutting capabilities, and sturdy construction. With its ability to perform different milling tasks, the knee mill is an essential tool in the manufacturing industry.
Specification
- Spindle Speed: Variable, 50 to 4,500 RPM
- Spindle Taper: R8 or NT30
- Table Size: Varies, around 9″ x 42″ or 10″ x 50″
- Longitudinal Travel: Varies, 24″ to 36″
- Cross Travel: Varies, 12″ to 16″
- Vertical Travel: Varies, 16″ to 18″
- Motor Power: Varies, 2 HP to 5 HP
- Weight: Varies, 2,000 lbs to 5,000 lbs
- Control: Manual or CNC
Pros
- Versatility: Knee mills are popular
- Precision: These mills offer excellent precision and accuracy, making them suitable
- Rigidity: Knee mills are typically built with a solid and sturdy structure
- Accessibility: The knee mill design allows for easy access
- Cost-effective: Knee mills are often more affordable compared
Cons
- Limited size and capacity
Definition And Features Of Bed Mill
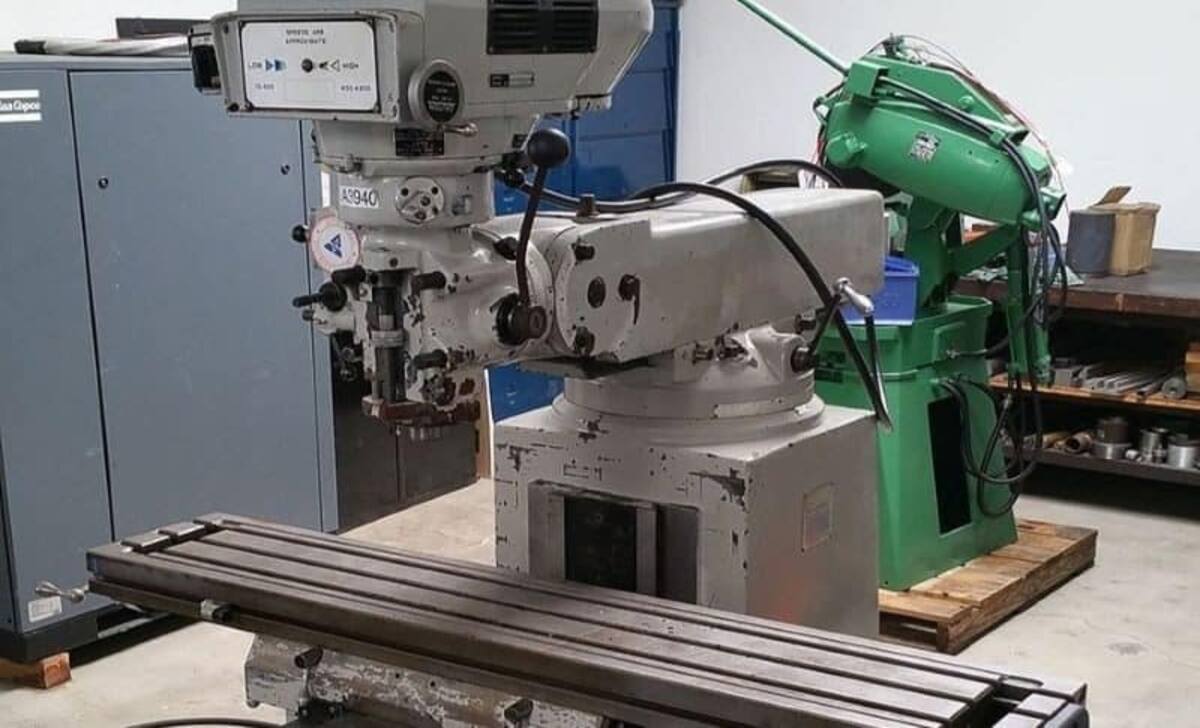

One of the main advantages of a knee mill is its versatility. The vertical movement of the worktable allows for the milling of complex shapes and angles, making it ideal for intricate and precise milling tasks. Additionally, the knee mill’s smaller footprint makes it suitable for smaller workshops with limited space. On the other hand, a bed mill offers greater stability and rigidity due to its fixed worktable. This stability allows for heavier cutting loads and larger workpieces, making it the preferred choice for heavy-duty milling operations.
Specification
- XAxis Travel: Varies (500mm to 3000mm)
- YAxis Travel: Varies (400mm to 1000mm)
- ZAxis Travel: Varies (400mm to 1000mm)
- Spindle Motor Power: Varies (5 HP to 30 HP)
- Spindle Speed Range: Varies (50 RPM to 5000 RPM)
- Table Size: Varies (600mm x 300mm to 2000mm x 1000mm)
- Table Load Capacity: Varies (500 kg to 5000 kg)
- Control System: CNC (Computer Numerical Control)
- Tool Capacity: Varies (10 to 30 tool positions)
- Machine Weight: Varies (2000 kg to 15000 kg)
- Dimensions: 2500mm x 2300mm x 2200mm
Pros
- Stability and Rigidity
- Larger Workpiece Capacity
- Cost-effective
Cons
- Limited Accessibility
Comparison Of Knee Mill Vs. Bed Mill
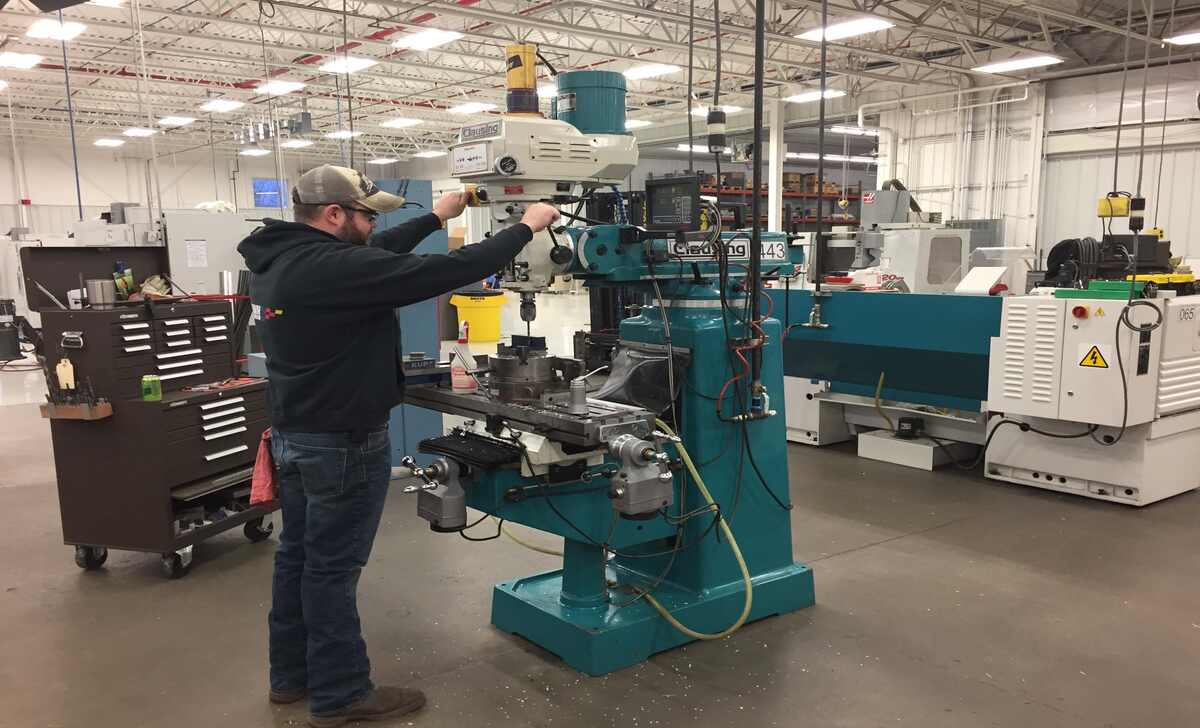

When comparing knee mills and bed mills, it is important to consider the types of milling machines available. Knee mills feature a vertical milling machine configuration, where the spindle head is positioned vertically. These machines are famous for their versatility and ability to handle various tasks.
On the other hand, bed mills have a horizontal spindle head and provide more stability and rigidity. Both milling machines can be equipped with power feed, enhancing efficiency and productivity. Overall, these machine tools play a crucial role in the machining industry, offering different advantages depending on the specific needs of the operations. Here, we discuss knee mill vs bed mill.
1. Differences In Design And Structure
One significant difference in knee and bed mills is their design and structure. Knee mills, also known as knee-type milling machines, feature an adjustable knee that allows vertical movement of the worktable. This provides flexibility in machining operations.
On the other hand, bed mills, commonly referred to as turret mills, have a fixed bed for the worktable. This design offers stability and rigidity, making them suitable for heavy-duty machining. People utilize both machines based on specific machining requirements, and they have their advantages.
2. Variations In Size And Capacity
When comparing knee mills to bed mills, variations in size and capacity become evident. Knee mills, equipped with a vertical knee and a manual milling head, offer versatility and flexibility. You can adjust the spindle speed to accommodate different materials and cutting requirements. On the other hand, bed mills provide a larger worktable and increased stability, making them suitable for heavy-duty machining tasks. Ultimately, the choice between knee and bed mills depends on the project’s specific needs.
3. Variation In Precision And Accuracy
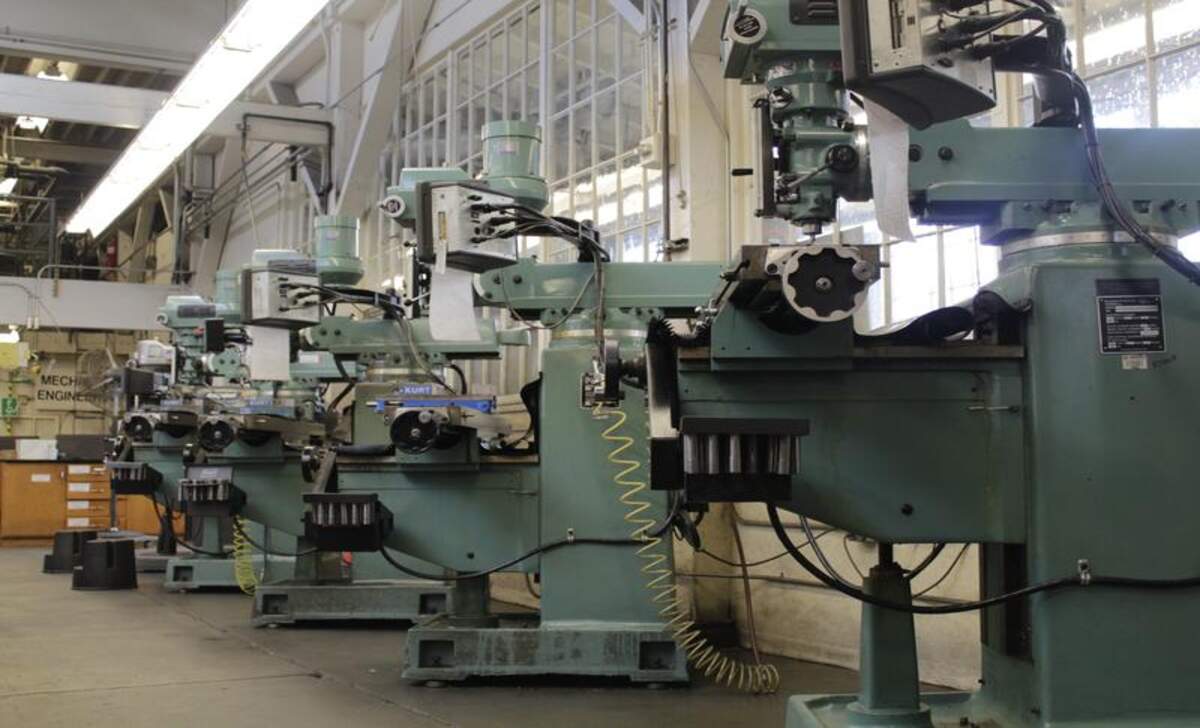

There is a notable difference between knee and bed mills regarding precision and accuracy. Knee mills, such as manual knee mills, offer a distinct advantage in terms of versatility and ease of use. These machines allow for precise adjustments and are ideal for smaller-scale projects. On the other hand, bed mills provide enhanced stability and rigidity, making them suitable for larger-scale operations. Ultimately, the choice between the two depends on the specific needs and requirements of the milling project.
4. Differences In Versatility And Application
Regarding versatility and application, there are distinct differences between knee mills and bed mills. Knee mills, with their movable knee, offer greater vertical movement and positioning flexibility. Smaller, more intricate tasks suit them well, and people often prefer them in toolrooms and prototyping.
On the other hand, bed mills, with their fixed bed and movable spindle, provide better stability and rigidity, making them suitable for heavy-duty machining operations and larger workpieces. Each type has its strengths and limitations, catering to the specific needs of different industries and applications.
5. Cost Considerations
The average price of knee and bed milling machines can vary significantly depending on several factors, such as brand, size, features, and quality. Generally, knee milling machines tend to be more affordable, with prices ranging from around $3,000 to $20,000.
On the other hand, bed milling machines, which are larger and offer more versatility and precision, can range from $20,000 to $100,000 or more. It’s important to note that these prices are just averages, and both cheaper and more expensive options are available in the market. Price can also be influenced by the type of milling machine (vertical or horizontal), its condition (new or used), and the seller’s location.
Applications And Industries
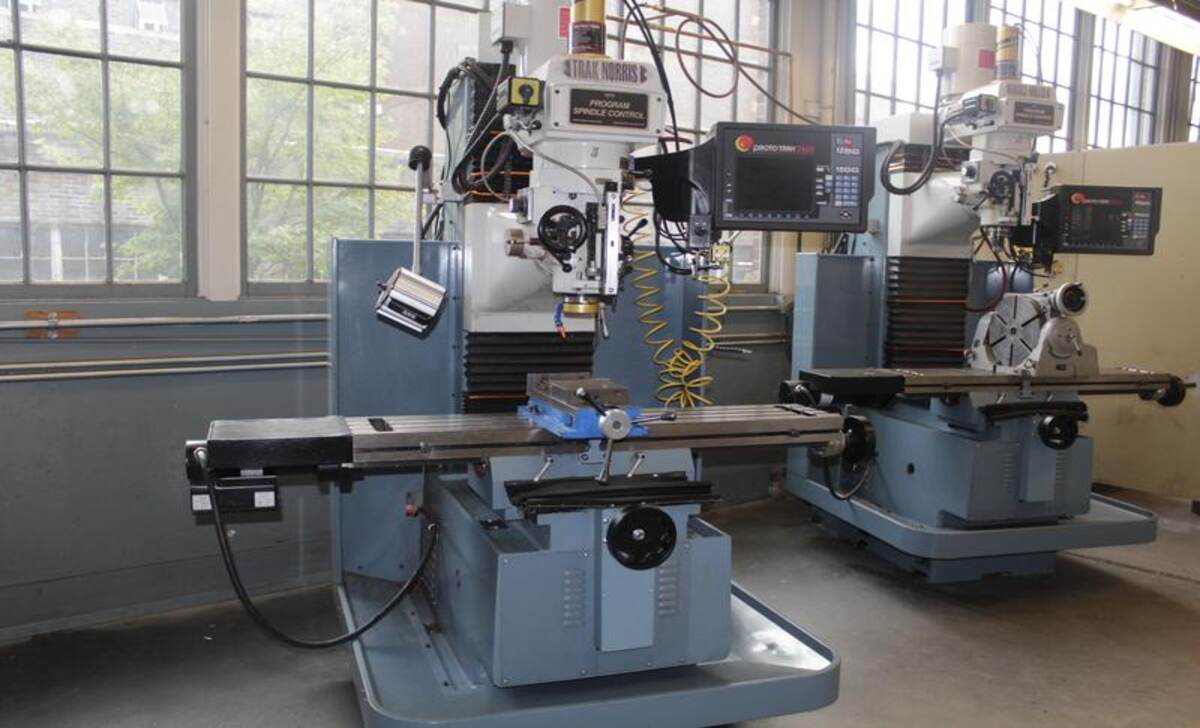

Knee mills are handy in the automotive, aerospace, and tool manufacturing industries. Their versatility makes them suitable for various applications, including drilling, boring, and milling operations. On the other hand, bed mills find extensive use in industries like construction, woodworking, and metal fabrication.
Their rigid structure allows for heavy-duty machining, making them ideal for cutting large pieces and producing complex shapes. Different industries have unique needs that are met by tailoring each mill type to specific applications.
Selection Factors
It’s crucial to evaluate your specific needs and requirements. Factors such as the workpiece’s size and weight, the machining operations’ complexity, and the desired precision level should be considered. You should also consider space availability, budget constraints, and the operator’s experience level. By carefully assessing these factors, you can make an informed decision that best suits your machining needs.
Case Studies And Examples
When comparing knee and bed mills, it is important to consider real-life examples and case studies to understand their applications and the results they can achieve. Regarding knee mill applications, they have been widely handy in the automotive, aerospace, and mold-making industries, where precision and versatility are crucial.
On the other hand, bed mills have found their applications in heavy-duty machining, such as large-scale production of components for construction and industrial machinery. By examining the results achieved by each type of mill, we can gain insights into their strengths and limitations, enabling us to make informed decisions based on specific project requirements.
Conclusion
Choosing between a knee mill and a bed mill ultimately depends on the specific needs and preferences of the operator. While a knee mill offers more versatility and flexibility, a bed mill provides better stability and accuracy for heavy-duty tasks.
Both of these machines have unique benefits and can greatly impact the efficiency and productivity of a machining operation. It is important to carefully consider the intended use and workload before deciding. Ultimately, both types of mills have advantages and can greatly benefit a machining operation. Consult with an experienced professional before making a final decision.
FAQs
1.What Is A Mill Bed?
Ans: A milling machine is mounted on a mill bed, a horizontal platform, or a surface. It provides a stable and rigid base for the machine, allowing it to perform various precision cutting, shaping, and drilling operations on workpieces.
2.What Is Automation In CNC?
Ans: Automation in CNC (Computer Numerical Control) refers to using technology and computer software to control and operate machines, such as lathes, milling machines, and routers, in manufacturing.
3.What Format Is A CNC Mill?
Ans: CNC mills use the XYZ coordinate system. This format is commonly referred to as XYZ, where X represents the horizontal movement, Y represents the vertical movement, and Z represents the depth or thickness of the cut material.
4.Is CNC A Mill Or A Lathe?
Ans: CNC refers to Computer Numerical Control, a technology used in milling and lathe machines. It allows for automated control and precise machining of materials.
5.Is CNC Laser Cutting?
Ans: CNC (Computer Numerical Control) laser cutting is a specific type of laser cutting process that uses a computer-controlled laser to cut materials precisely.
