Milling is a crucial process in the manufacturing industry, used to create precise and complex shapes on various materials. The two most commonly used milling methods are face milling and peripheral milling.
While both techniques involve removing material from a workpiece, their approach and application differ. Understanding the differences between face and peripheral milling is crucial for selecting the appropriate method for a specific project.
We will delve into the specifics of both techniques and the difference between face milling and peripheral milling. We will also explore the various applications where each method excels, allowing you to decide which method is best suited for your milling needs.

Definition And Purpose Of Face Milling
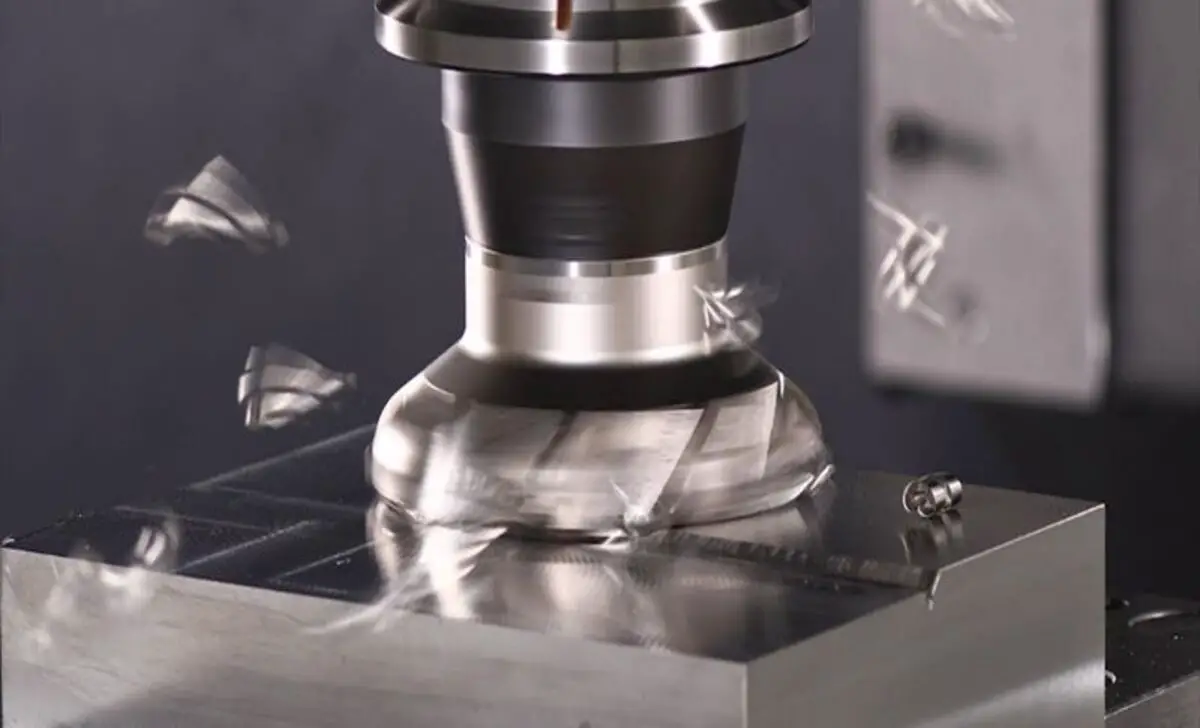

Face milling is a machining process involving milling cutters to remove material from flat surfaces. It is commonly used to create smooth and even finishes on workpieces. The purpose of face milling is to improve the surface quality and accuracy of the machined part. By employing the right milling cutters and techniques, face milling can efficiently shape and refine flat surfaces, resulting in precise and visually appealing outcomes.
Feature
- Efficient material removal
- Smooth and even finish
- Creates flat surfaces, slots, and pockets
- Works on metals, plastics, and composites
- High productivity and cutting speeds
- Precise and accurate machining
- Versatile for roughing and finishing
Pros
- The high material removal rate
- Improved surface finish
- Versatility: Face milling can be performed
- Cost-effective: Face milling is a cost-effective method
Cons
- Limited to flat surfaces
- Tool wear
Definition And Purpose Of Peripheral Milling
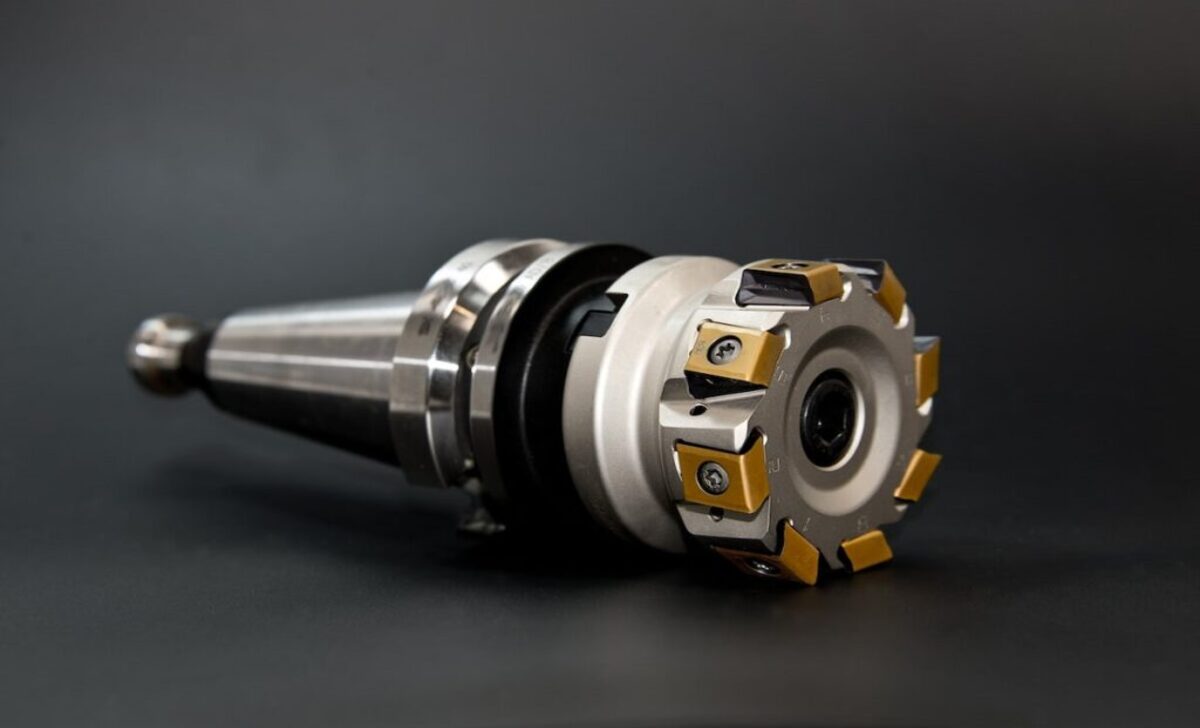

Peripheral milling, also known as edge milling, is a machining process that involves removing material from the periphery of a workpiece using a rotating cutting tool. The purpose of peripheral milling is to create smooth and accurate surfaces and shape and contour the workpiece.
This process is commonly used in automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing industries, where precision and dimensional accuracy are crucial. By carefully controlling the milling process, operators can achieve desired shapes, sizes, and finishes on the workpiece, making it suitable for various applications.
Feature
- Peripheral milling: removes material from the workpiece periphery
- Used in milling machines for shapes, contours, profiles
- The cutting tool rotates on the axis, removes material
- Efficient material removal, high precision
- Suitable for metal, plastic, wood
- Versatility in cuts, shapes
- Multiple teeth for faster speeds improved productivity
- Used in automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing industries
Pros
- The high material removal rate
- Versatility: This milling technique is suitable
- Improved surface finish
- Cost-effective
Cons
- Limited accessibility
- Tool wear and heat generation
Differences Between Face Milling Vs Peripheral Milling

Various approaches can be utilized for milling operations, each with advantages and disadvantages. Two common techniques used in machining are face milling and peripheral milling. While both methods involve removing material from a workpiece using a rotating cutter, the two have distinct differences.
1.Cutting Direction And Tool Path Variations
When comparing face milling and peripheral milling, there are notable differences in cutting direction and tool path variations. Face milling involves milling the surface of a workpiece using a cutter that rotates perpendicular to the workpiece.
On the other hand, peripheral milling involves milling the periphery of the workpiece using a cutter that rotates in a parallel direction. These variations in the milling process impact the efficiency and effectiveness of the machining process. Additionally, selecting appropriate milling tools is crucial in achieving desired results in both face and peripheral milling.
2.Surface Finish And Accuracy Differences
Surface finish and accuracy play crucial roles in milling applications. There are distinct differences to consider when comparing face milling and peripheral milling techniques. Face milling involves using a milling cutting tool that rotates perpendicular to the workpiece surface, resulting in a smooth and flat finish.
On the other hand, peripheral milling utilizes a cutting tool that rotates parallel to the workpiece surface, allowing for greater precision in milling. The choice between these techniques depends on the desired outcome and specific project requirements.
3.Material Removal Rates And Cutting Forces Comparison
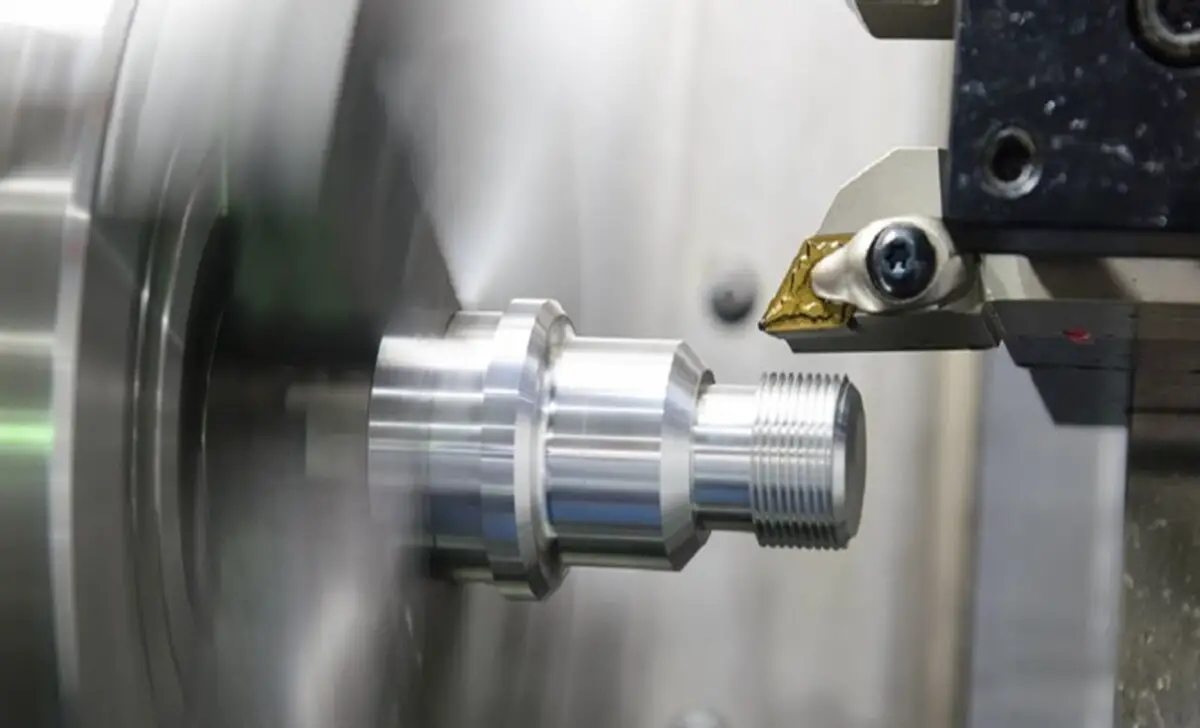

One notable difference between face and peripheral milling is in the material removal rates and cutting forces involved. The timely milling technique is employed in face milling, where the cutter rotates in the same direction as the feed, resulting in efficient chip evacuation and increased material removal rates.
On the other hand, peripheral milling utilizes climb milling, where the cutter rotates against the feed direction, reducing cutting forces and enhancing tool life. These distinctions are crucial in determining the most suitable milling method for specific applications.
4.Tool Life And Chip Evacuation Considerations
When considering face and peripheral milling, it is important to consider key factors such as tool life and chip evacuation. Face milling involves cutting across the face of the workpiece, while peripheral milling focuses on cutting along the edges.
These techniques have distinct differences in tool wear and the ability to remove chips effectively. Understanding these variations is crucial for optimizing machining processes and achieving desired results. Analyzing tool life and chip evacuation factors will ensure efficient and successful milling operations.
5.Price Comparison
The average price of face milling compared to peripheral milling varies depending on factors such as the specific machining requirements and the size and complexity of the job. Face milling generally involves larger, more sophisticated machines and tools, which can result in higher costs than peripheral milling.
The best place to find the average prices for face and peripheral milling is through industry suppliers and manufacturers, who can provide quotes and pricing information based on specific project requirements.
Factors Influencing The Choice Between Face Milling And Peripheral Milling
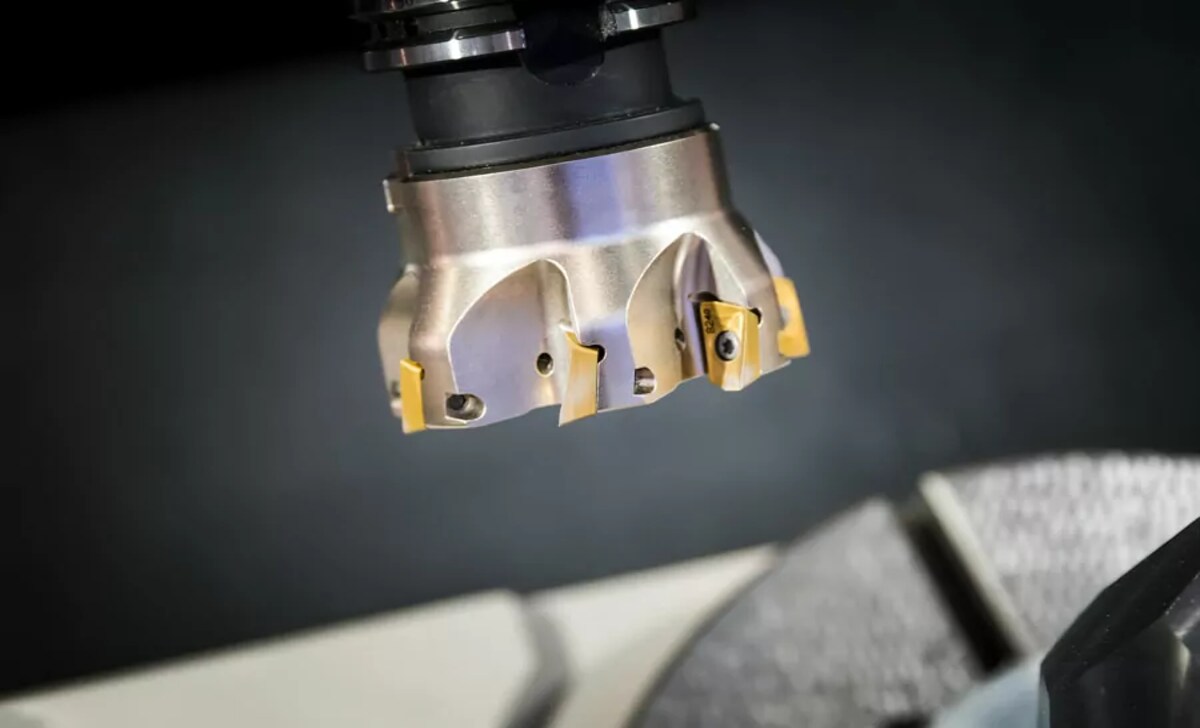

Several factors come into play when deciding between face milling and peripheral milling. Firstly, the characteristics and geometry of the workpiece are crucial in determining the most suitable milling method. Secondly, one must consider the type and hardness of the milled material.
Additionally, the desired surface finish and accuracy requirements are significant in decision-making. Finally, production volume and time constraints must also be considered to ensure efficient and timely milling operations. These factors collectively influence the ultimate choice between face milling and peripheral milling.
Case Studies Or Examples
Face milling and peripheral milling are two common techniques handy in the machining industry. Face milling is applied in various scenarios, such as when creating flat surfaces, producing large flat areas, or machining large workpieces. Examples of face milling include the production of engine blocks, construction equipment components, and aerospace parts.
On the other hand, peripheral milling is handy for tasks like contouring, slotting, and creating intricate shapes. This technique is commonly employed in manufacturing gears, molds, and automotive components. Understanding the differences and applications of face and peripheral milling can help manufacturers choose the most suitable method for their specific machining needs.
Conclusion
The face and peripheral milling have advantages and can be suitable for different machining operations. While face milling is ideal for creating flat surfaces and decreasing cycle time, peripheral milling is better for producing complex shapes and achieving higher precision.
While both face and peripheral milling have strengths, machinists must understand the differences and choose the appropriate technique for their specific project needs. Machinists must understand the differences between these two milling techniques and choose the appropriate one for their specific project needs. Ultimately, both methods have their place in machining and can lead to successful and efficient production processes.
FAQ
1.What Is Peripheral Milling?
Peripheral milling is an operation where the cutting tool rotates on its axis and moves along the periphery of the workpiece. This milling technique removes material from the workpiece’s outer edges, creating a flat surface or a specific shape.
2.What Is The Principle Of A Milling Machine?
The principle of a milling machine is to remove material from a workpiece by rotating a cutting tool against it. This cutting tool, a milling cutter, is mounted on a spindle and can be moved in multiple directions to achieve precise cuts and shapes.
3.What Is High-Efficiency Milling?
High-efficiency milling (HEM) is a machining technique that involves using high speeds, feeds, and depths of cut to remove material quickly and efficiently. It typically utilizes smaller cutting tools with multiple flutes to increase material removal rates while maintaining tool life.
4.What Is The Equipment For Milling?
The equipment used in milling typically includes a machine, which is a power-driven machine equipped with cutting tools, such as end mills or face mills, used to remove material from a workpiece to create the desired shape or surface.
5.What Is Mill Speed?
Mill speed is the rotational speed at which a mill, such as a grinding mill or a milling machine, operates. It is typically measured in revolutions per minute (RPM).