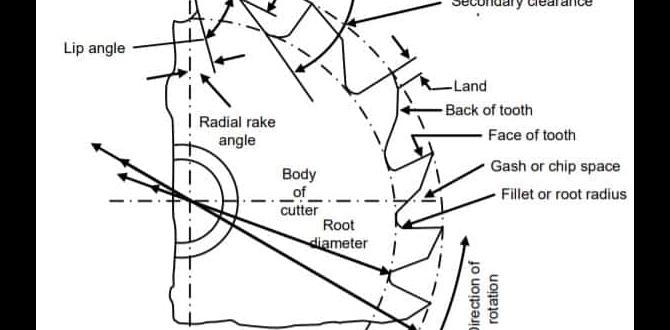
Have you ever wondered about the magic of turning old, rusty machines into shining tools again? Lathe restoration can do just that! Imagine taking a worn-out metal lathe and giving it a brand-new life. It’s like turning back time on a forgotten treasure.
But how does one go about this exciting process? Many enthusiasts start by using CAD design tools. These tools help plan and visualize every detail before getting started. It’s fascinating to think that a simple drawing can lead to incredible changes in real life.
Whether you are a beginner or a seasoned pro, lathe restoration can captivate anyone. The journey of fixing a metal lathe is filled with surprises and rewards. By the end, you might be surprised at how much you learn and create!
So, are you ready to dive into the world of lathe restoration? Get ready to discover tips, tricks, and secrets that will help you bring your metal lathe back to life.
Lathe Restoration: Metal Lathe Cad Design Techniques

Lathe Restoration: Metal Lathe CAD Design Insights
Restoring a metal lathe is an exciting challenge. It blends skill, patience, and creativity. With CAD design, you can visualize parts before making them. This process helps identify necessary upgrades and repairs. Have you ever wondered how a simple lathe transforms raw metal into precise shapes? Proper tools and designs can make a big difference. With a little effort, a worn-out lathe can become a masterpiece in your workshop!Understanding Lathe Restoration Basics
Definition and importance of lathe restoration. Common issues faced in metal lathes.Lathe restoration is like bringing a tired old car back to life. It means fixing and improving metal lathes, which are important for shaping metal. This process makes machines run better and last longer. Common problems include worn-out parts and rust, which can make them grumpy. Luckily, with some care, you can turn that cranky lathe into a happy, smooth operator!
| Common Issues | Possible Solutions |
|---|---|
| Worn bearings | Replace or lubricate |
| Rusty surface | Sand and paint |
| Broken belts | Replace with new belts |
Tools and Materials for Lathe Restoration
Essential tools needed for restoration. Recommended materials for repairs and enhancements.Restoring a lathe? Time to gather some cool tools! You’ll need wrenches, screwdrivers, and maybe even a rubber chicken for motivation! The main materials for repairs are bearings, belts, and any metal parts that look like they’ve been through a war. These will help you breathe new life into your lathe. Here’s a quick list of essentials:
| Tools | Materials |
|---|---|
| Wrench Set | Bearings |
| Screwdrivers | Belts |
| Measuring Tools | Metal Stock |
Remember, the right tools and materials make all the difference. So, arm yourself wisely!
Step-by-Step Restoration Process
Disassembly: Best practices for safe and effective breakdown. Cleaning: Techniques for thorough cleaning of components.Disassembling a lathe? It sounds tricky, but with the right steps, you can be the king of breakdowns! Start by taking notes or photos of each part. You won’t want to wonder later where that mysterious tiny screw goes! Use a clean workspace to avoid losing pieces—trust me, your carpet doesn’t need more lathe parts. Once disassembled, it’s time for a deep clean!
For cleaning, gather some brushes and safe cleaning solutions. Use them to scrub away grime and grease. A warm soapy water bath is great for smaller parts. Don’t forget to dry everything thoroughly—no one likes rust making an unwanted appearance! Soon, you’ll have shiny, usable pieces ready for reassembly.
| Step | Tip |
|---|---|
| Disassemble | Label parts as you go! |
| Clean | Use warm, soapy water! |
Assessing and Repairing Damage
Identifying common types of damage. Methods for repairing or replacing damaged parts.To spot damage, look for rust, broken parts, or wear on the metal lathe. Common issues include:
- Worn bearings
- Cracked bed
- Dull cutting tools
For repairs, you can either fix or replace parts. Use replacement kits for bearings. Weld cracks for a strong fix. Always clean before starting any repairs. Following these steps helps keep your lathe in great shape.
What are common types of damage on a metal lathe?
Common damage includes rust, broken components, and worn parts. Regular checks can prevent bigger issues later.
How can damaged parts be repaired or replaced?
To repair, clean and weld cracks. For replacement, use kits available online or at stores. Always ensure proper measurements before buying new parts.
Designing Custom Parts using CAD
Process of creating 3D models for lathe components. Tips for ensuring precision in designs for restoration.Creating 3D models for lathe components is like being a magician. With CAD software, you can shape metal like playdough! Start by sketching your ideas. Then, use CAD to turn those doodles into detailed designs. Precision is key, so double-check your measurements. You don’t want parts that fit like a square peg in a round hole! For added fun, remember to save your work often—losing your design is as sad as losing your favorite toy.
| Tip | Description |
|---|---|
| Measure Twice | Always check your dimensions before finalizing your design. |
| Test & Iterate | Make prototypes and adjust your design as needed. |
| Use Guides | Follow CAD tutorials to sharpen your skills. |
Integrating Modern Technology in Lathe Restoration
Benefits of using CNC technology in restoration. Examples of modern upgrades for vintage lathes.Adding modern tech to lathe restoration is like giving an old dog a trendy haircut—it looks fabulous! Using CNC technology helps in precision. This means your cuts are smoother, and accuracy is top-notch. Plus, vintage lathes can get fun upgrades like digital readouts and automatic feeds. It’s like having a fancy coffee machine, but for metal!
| Upgrade | Benefit |
|---|---|
| CNC Control | Improved precision |
| Digital Readout | Easy measurements |
| Automatic Feeds | Less manual effort |
These updates can make an old lathe feel brand new! So, why let that vintage tool collect dust? Time for a makeover!
Testing and Calibration of Restored Lathes
Importance of calibration after restoration. Procedures for testing functionality and accuracy.After you restore a lathe, testing and calibration are crucial. Think of it as tuning a musical instrument. If it’s off, your work might hit a sour note! Calibration ensures that your lathe performs accurately. Start by checking its alignment and measure its speed and precision. If something seems off, don’t panic; adjustments are part of the process!
| Testing Procedure | Description |
|---|---|
| Check Alignment | Ensure all parts are aligned properly for smooth operation. |
| Measure Speed | Confirm the lathe’s speed matches the set parameters. |
| Test Precision | Use a caliper to ensure accurate measurements on finished pieces. |
Remember, a well-calibrated lathe makes for happy projects! So, don’t skip this step, or you might end up with a wobbly creation. Besides, who wants a lathe that can’t keep its cool?
Maintenance Tips for Longevity of Restored Lathes
Regular maintenance routines to follow. How to troubleshoot common issues postrestoration.To keep your restored lathe running smoothly, follow these easy maintenance steps. Clean it often to remove dirt and dust. Check oil levels and add more if needed. Tighten loose screws and bolts. Regularly inspect belts and gears too.
- Lubricate moving parts.
- Keep electrical connections secure.
- Use covers to protect from dust.
If you run into problems, check these tips:
- For noise, check for loose parts.
- If it won’t start, ensure it’s plugged in.
- Inspect for worn belts if things feel stiff.
Remember, regular care makes your lathe last longer!
What are some common issues after restoration?
Common problems include noise, failure to start, and stiff movements. Always inspect wiring, lubricate parts, and check belts.
Conclusion
In summary, lathe restoration and CAD design are exciting ways to bring old tools back to life. You can learn new skills by restoring a metal lathe. Using CAD software helps you design parts more accurately. We encourage you to explore resources to start your own project. With hands-on practice, you’ll gain confidence and create something fantastic!FAQs
What Are The Essential Steps Involved In Restoring A Vintage Metal Lathe To Working Condition?To restore a vintage metal lathe, start by cleaning it. Use a cloth to remove dirt and grease. Next, check for any broken parts and replace them if needed. After that, oil all the moving parts so they work smoothly. Finally, test the lathe to make sure it runs well.
How Can Cad Software Be Utilized To Design Custom Parts For A Metal Lathe Restoration Project?You can use CAD software to create detailed drawings of metal parts. First, you can measure the old parts you want to replace. Next, you draw the new part on the computer, making sure it fits just right. Then, you can save and print the design to make the new part for your lathe. This helps make your project easier and more accurate!
What Materials Are Commonly Recommended For Replacing Worn Or Damaged Components In A Metal Lathe?For replacing worn or damaged parts in a metal lathe, you can use several materials. Steel is strong and good for many parts. Aluminum is lighter and easier to work with. Bronze is helpful for making bearings that need to move smoothly. Using the right material helps your lathe work better and last longer.
What Are The Best Practices For Measuring And Creating Accurate Cad Models Of Existing Lathe Parts?To create accurate CAD models of lathe parts, start by carefully measuring each part with a ruler or caliper. Write down the measurements so you don’t forget them. Next, use CAD software to draw the parts based on your measurements. Always check your work to make sure it matches the real part. Finally, ask someone to review your model to catch any mistakes.
How Do You Determine The Optimal Specifications For New Components When Designing For A Metal Lathe Using Cad?To find the best parts for a metal lathe, we start by thinking about what we need the machine to do. Then, we can use computer programs called CAD, which stands for Computer-Aided Design, to draw our ideas. We try different sizes and shapes to see what works best. After that, we can test our designs to make sure they fit and work well together. Finally, we choose the designs that help the lathe perform its job effectively.
{“@context”:”https://schema.org”,”@type”: “FAQPage”,”mainEntity”:[{“@type”: “Question”,”name”: “What Are The Essential Steps Involved In Restoring A Vintage Metal Lathe To Working Condition? “,”acceptedAnswer”: {“@type”: “Answer”,”text”: “To restore a vintage metal lathe, start by cleaning it. Use a cloth to remove dirt and grease. Next, check for any broken parts and replace them if needed. After that, oil all the moving parts so they work smoothly. Finally, test the lathe to make sure it runs well.”}},{“@type”: “Question”,”name”: “How Can Cad Software Be Utilized To Design Custom Parts For A Metal Lathe Restoration Project? “,”acceptedAnswer”: {“@type”: “Answer”,”text”: “You can use CAD software to create detailed drawings of metal parts. First, you can measure the old parts you want to replace. Next, you draw the new part on the computer, making sure it fits just right. Then, you can save and print the design to make the new part for your lathe. This helps make your project easier and more accurate!”}},{“@type”: “Question”,”name”: “What Materials Are Commonly Recommended For Replacing Worn Or Damaged Components In A Metal Lathe? “,”acceptedAnswer”: {“@type”: “Answer”,”text”: “For replacing worn or damaged parts in a metal lathe, you can use several materials. Steel is strong and good for many parts. Aluminum is lighter and easier to work with. Bronze is helpful for making bearings that need to move smoothly. Using the right material helps your lathe work better and last longer.”}},{“@type”: “Question”,”name”: “What Are The Best Practices For Measuring And Creating Accurate Cad Models Of Existing Lathe Parts? “,”acceptedAnswer”: {“@type”: “Answer”,”text”: “To create accurate CAD models of lathe parts, start by carefully measuring each part with a ruler or caliper. Write down the measurements so you don’t forget them. Next, use CAD software to draw the parts based on your measurements. Always check your work to make sure it matches the real part. Finally, ask someone to review your model to catch any mistakes.”}},{“@type”: “Question”,”name”: “How Do You Determine The Optimal Specifications For New Components When Designing For A Metal Lathe Using Cad? “,”acceptedAnswer”: {“@type”: “Answer”,”text”: “To find the best parts for a metal lathe, we start by thinking about what we need the machine to do. Then, we can use computer programs called CAD, which stands for Computer-Aided Design, to draw our ideas. We try different sizes and shapes to see what works best. After that, we can test our designs to make sure they fit and work well together. Finally, we choose the designs that help the lathe perform its job effectively.”}}]}