Cedar siding is a popular choice for homeowners due to its durability, natural beauty, and resistance to pests. However, one issue that can arise with cedar siding is mould growth.
Not only does mould detract from the aesthetic appeal of your home, but it can also pose serious health risks to you and your family. Mold is a fungus that thrives in moist environments and can spread quickly on cedar siding, especially in damp or humid climates. Once mould has taken hold, removing and preventing it from recurring can be challenging.
Here, we will discuss the causes of mould growth on cedar siding and provide effective methods for preventing and removing it. Whether you are a homeowner, contractor, or property manager, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and tools necessary to maintain the beauty and integrity of your cedar siding.

Step-By-Step Instructions For Turning Brass On The Wood Lathe
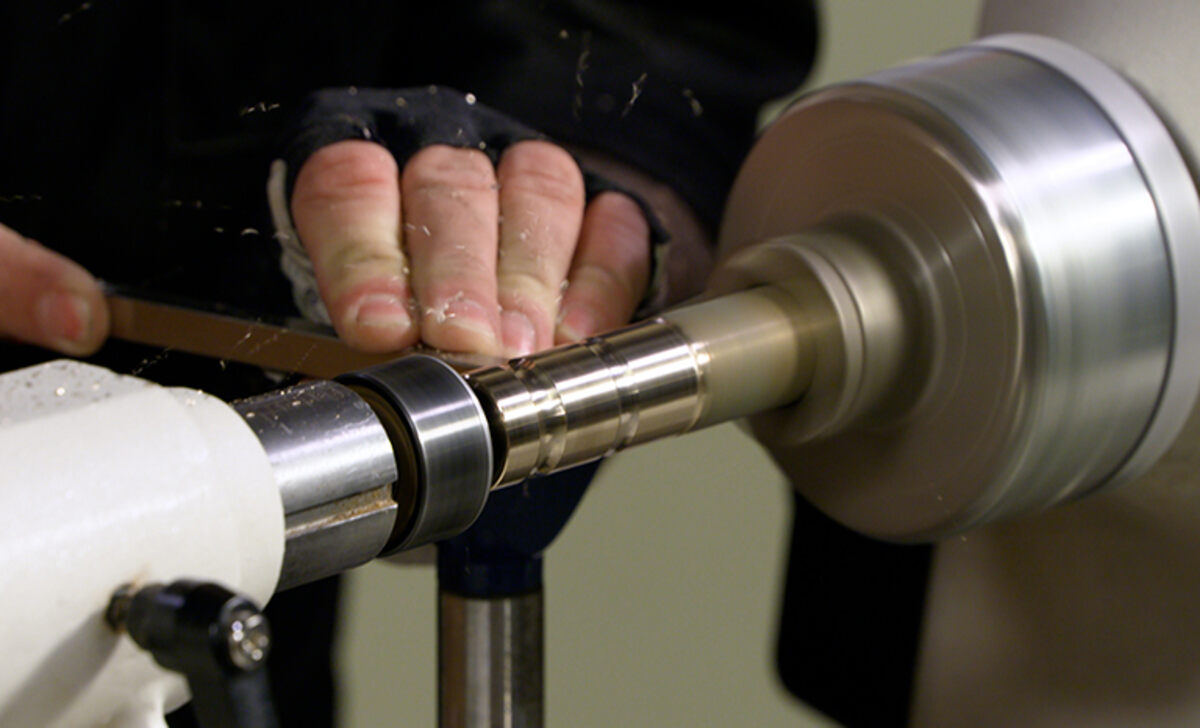

Turning brass on a wood lathe is a fascinating process that combines the precision of metalworking with the craftsmanship of woodworking. The wood lathe, a versatile tool typically used for shaping and carving wood, can turn brass into intricate and functional objects.
Brass, a metal alloy composed of copper and zinc, offers a unique opportunity for creative expression due to its malleability and attractive golden hue. You can create beautiful brass pieces with the right techniques to showcase your craftsmanship. Here are step-by-step instructions for turning brass on a wood lathe:
Safety Precautions And Equipment Needed
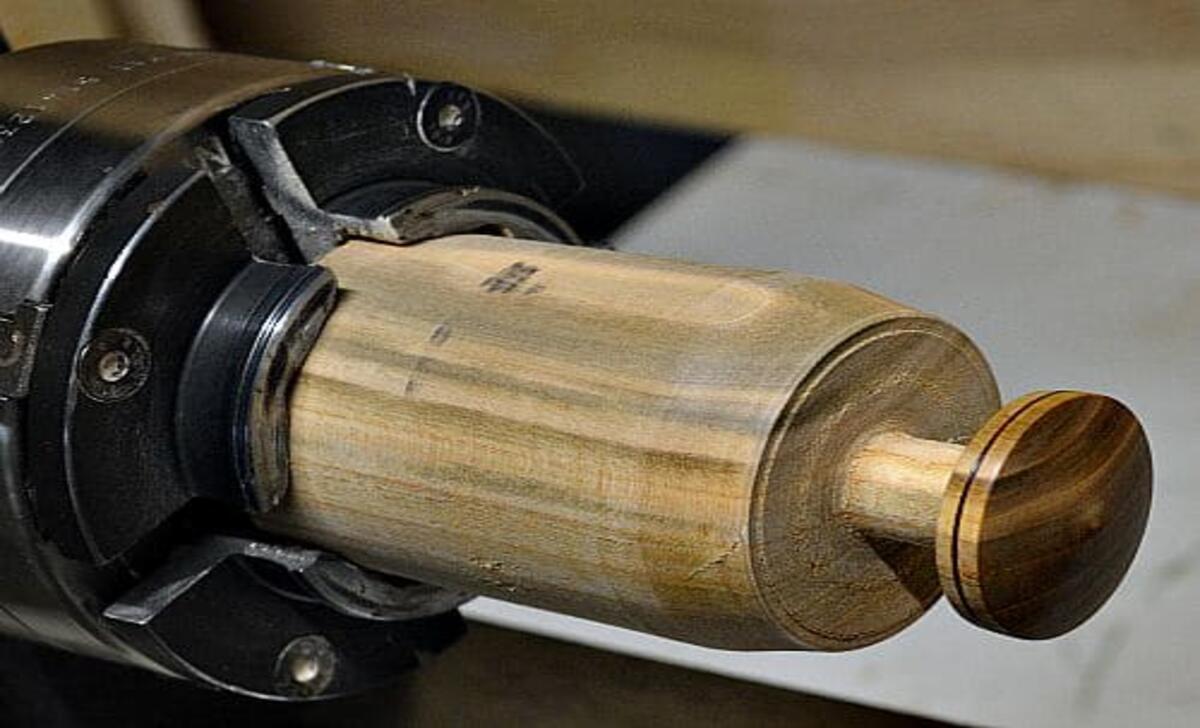

Turning brass on a wood lathe involves working with a metal material, so taking proper safety precautions is important. Here are some essential safety tips and equipment you’ll need:
- Always wear a face shield and protective eyewear to shield your face and eyes from flying chips or shavings.
- Use a tool holder or work-holding device to secure metal workpieces on a wood lathe.
- Consider the soft metal nature of brass when choosing lathe tools. We recommend using high-speed steel (HSS) or carbide-tipped tools for turning brass.
- Understand the properties of brass, such as its lower melting point, to ensure safe and accurate turning.
- Secure the workpiece firmly using a chuck or faceplate to avoid accidents during turning.
Mounting And Securing The Brass On The Lathe
When mounting brass on the wood lathe, it is essential to use the lathe chuck or faceplate securely. The tailstock can provide support for longer brass workpieces, ensuring balance and centring before turning. Properly securing the brass workpiece is crucial for turning accuracy, so consider using a brass-friendly chuck for a secure mount.
This precision-driven process involves woodworking projects and requires safety precautions such as wearing a face shield and using a tool holder to avoid accidents. Understanding the nature of soft metal, like brass, is vital for choosing the right tools and techniques for turning without chatter or accidents.
Mounting And Securing The Brass On The Lathe
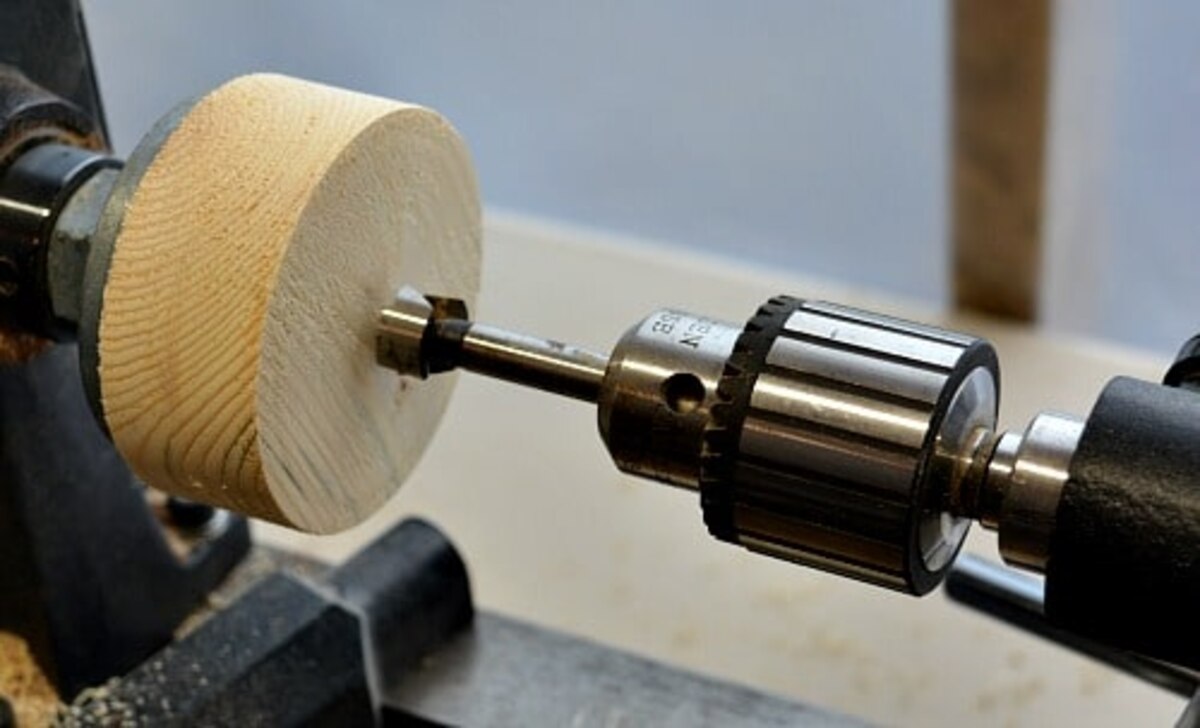

When turning brass on a wood lathe, it is important to properly mount and secure the brass to ensure safe and accurate machining. Here are some step-by-step instructions for mounting and securing brass on the lathe:
- Prepare The Brass: Select a piece suitable for turning on a lathe. Make sure the brass is clean and free from any debris or contaminants.
- Choose The Appropriate Chuck Or Faceplate: Depending on the size and shape of your brass piece, you must select the appropriate chuck or faceplate to attach to the lathe. Ensure that the chuck or faceplate is securely fastened to the lathe spindle.
- Mark The Centre Point: Use a centre punch or marking tool to make a small indentation at the centre of your brass piece. This will help you align it accurately on the lathe.
- Mount The Brass: Place your brass piece onto the chuck or faceplate, aligning the centre mark with the centre of the chuck or faceplate. Tighten any screws or jaws to secure the brass in place.
- Balance And Align: Check for any imbalance or misalignment once your brass is mounted. Adjust as necessary by loosening and re-positioning the screws or jaws.
- Test Run: Before starting your actual turning process, do a test run at low speed to ensure that everything is properly secured and aligned. Make any necessary adjustments before proceeding.
Choosing The Right Tools For Turning Brass
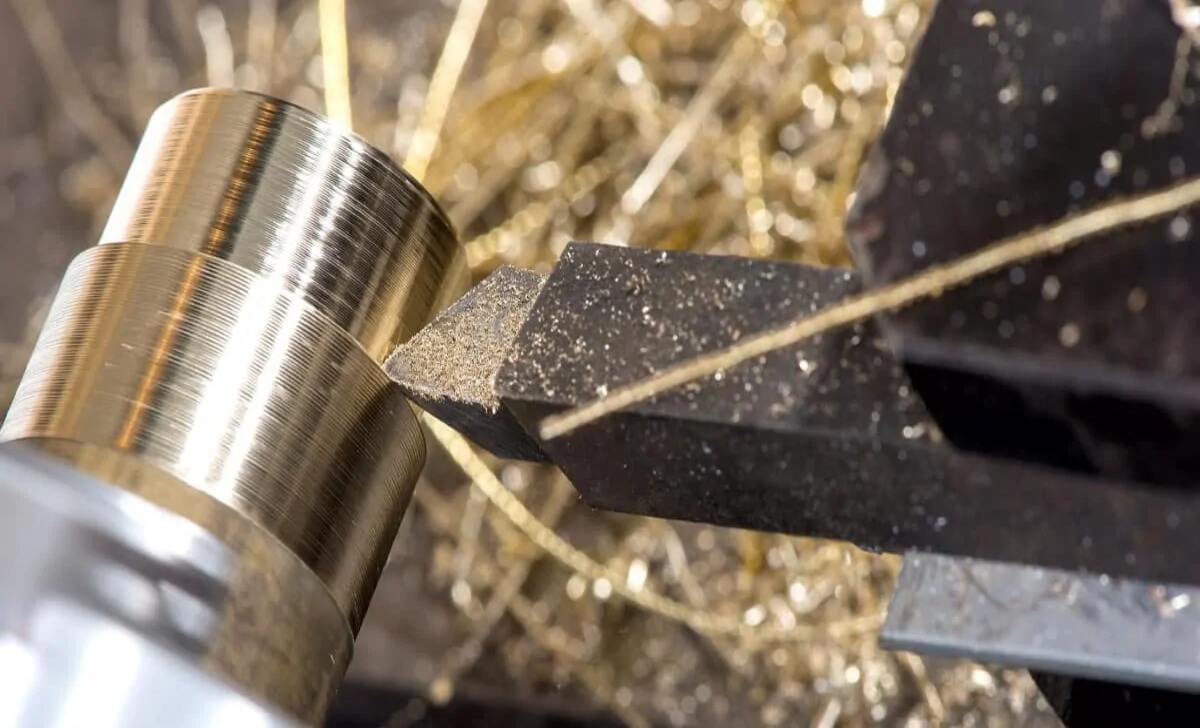

When turning brass on a wood lathe, choosing the right tools is crucial for achieving optimal results. Brass is a dense and tough material, requiring tools that can withstand its hardness and provide clean cuts. Carbide-tipped tools are often recommended for turning brass, as they have sharp cutting edges that can easily remove material without dulling quickly.
High-speed steel tools can also be used but may need more frequent sharpening. It’s important to select tools with appropriate angles and profiles for the specific cuts you want to make. Additionally, lubrication, such as cutting oil or wax, can help reduce heat and friction during turning.
Basic Turning Techniques For Brass
Turning brass requires slight adjustments to your techniques compared to woodworking. Here are some basic techniques to keep in mind:
- Take light cuts when turning brass to prevent tool chatter and reduce the risk of damage to the workpiece.
- Brass conducts heat quickly, so high speed and light pressure help prevent overheating and extend tool life.
- Lubrication is essential for turning brass smoothly. Apply cutting oil or beeswax frequently to reduce friction and improve the cutting surface.
- Pay close attention to tool positioning and cutting angles. Sharp tools and proper technique are crucial for achieving clean cuts on brass.
- Once turning is complete, sand the brass workpiece with increasingly finer grits of sandpaper, then buff or polish for a smooth, professional finish.
Creating Basic Shapes And Profiles

Creating basic shapes and profiles is an important step when turning brass on a wood lathe. Before beginning, ensure you have the necessary safety equipment, such as goggles and gloves, to protect yourself from flying debris. Start by securing the brass blank firmly in the chuck of the lathe.
Begin turning slowly and use a roughing gouge to remove excess material and create a cylindrical shape. Switch to smaller gouges or scrapers to refine the shape and create specific profiles or details as you progress. Take time and work slowly, making small adjustments to achieve your desired shape. You can create beautiful and intricate designs when turning brass on the wood lathe with practice and patience.
Adding Decorative Details And Textures
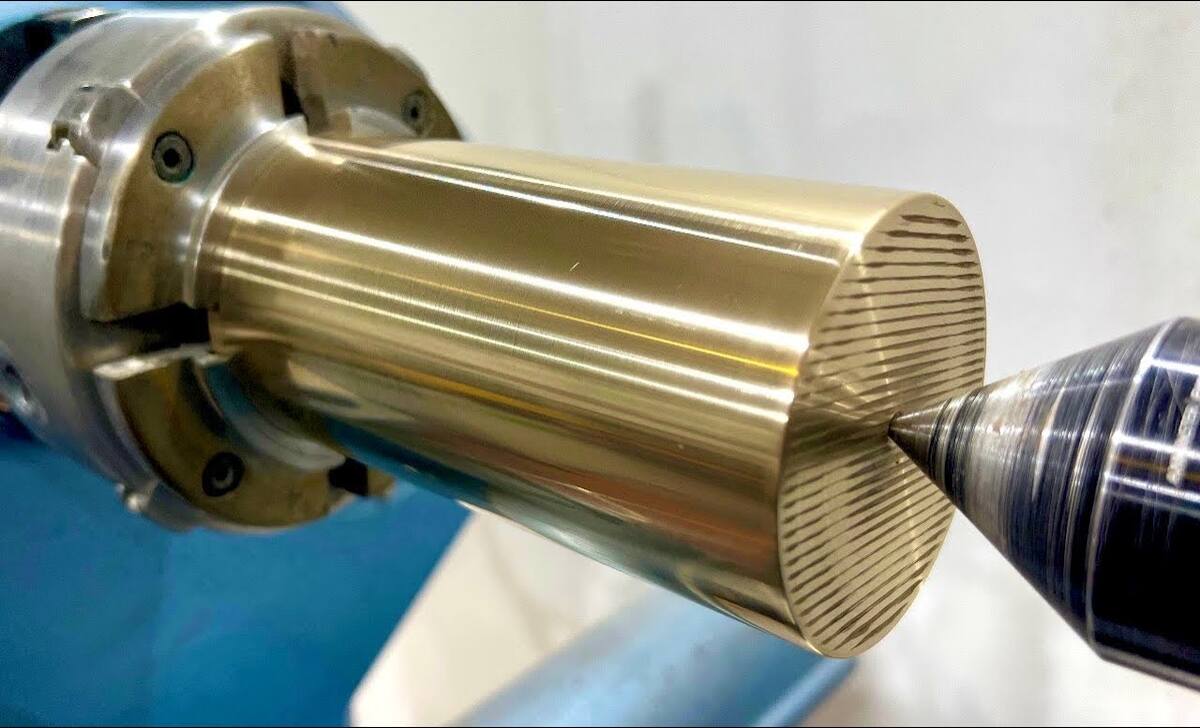

Adding decorative details and textures to brass turnings on a wood lathe can elevate the overall aesthetic of the finished piece. Various techniques can be used to achieve this, such as using specialized turning tools or adding embellishments like beads or wire.
One popular method is using texturing tools to create patterns and designs on the surface of the brass. This can be done by pressing the tool into the spinning brass, creating unique textures and visual interest. Another option is to use engraving tools to carve intricate designs directly onto the brass. This allows for even more customization and personalization of the final piece.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
When turning brass on a wood lathe, it is common to encounter certain issues that may affect the quality of your work. Here are some common problems that you may come across and how to troubleshoot them:
- Chatter: Chatter refers to the vibration or bouncing of the tool against the brass, resulting in an uneven surface. To reduce chatter, ensure your lathe is properly balanced and securely mounted. Additionally, check that your tool rests at the correct height and angle for optimal support.
- Tool Dullness: Brass can quickly dull cutting tools due to its abrasion. If your cuts are becoming less clean or more difficult to make, it may be time to sharpen or replace your tools.
- Chip Buildup: Brass produces long, stringy chips that can quickly accumulate around the workpiece and tool rest. To prevent chip buildup, ensure that your lathe’s chip deflector is properly positioned and consider using a dust collection system or shop vacuum to remove chips as you work.
- Heat Generation: When turning brass, friction can generate significant heat, which may cause warping or melting of the material. To minimize heat buildup, use sharp tools and light cuts to reduce the contact time between the tool and the brass.
Tips For Maintaining And Caring For Your Lathe And Tools
Maintaining and caring for your lathe and tools ensures longevity and optimal performance. Here are some tips to help you keep your lathe and tools in great shape:
- Keep Your Lathe Clean: Regularly clean your lathe to remove dust, debris, and any buildup of residue. Use a soft cloth or brush to wipe down the surfaces and remove excess oil or grease.
- Lubricate Moving Parts: Apply lubricant to the moving parts of your lathe, such as the spindle and tailstock, to ensure smooth operation. Be sure to use a lubricant recommended for use on metal surfaces.
- Sharpen Your Tools Regularly: Dull tools can lead to poor cutting performance and be dangerous. Keep your turning tools sharp by regularly sharpening them with a sharpening system or honing guide.
- Store Tools Properly: When not in use, store your turning tools in a clean, dry place to prevent rust or damage. Consider using tool racks or holders to keep them organized and easily accessible.
- Check For Wear And Tear: Regularly inspect your lathe and tools for any signs of wear or damage. Replace any worn-out parts or tools to maintain optimal performance and safety.
Conclusion
Turning brass on a wood lathe requires proper safety precautions, tools, and basic turning techniques. Following step-by-step instructions, you can create beautiful shape profiles and add decorative details to your brass projects. Remember to troubleshoot common issues and maintain your lathe and tools for optimal performance.
Now that you have a comprehensive understanding of turning brass on a wood lathe, you can confidently embark on your brass-turning journey. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced woodworker, exploring the possibilities of working with brass on a lathe can open up new creative avenues for your projects. So, grab your tools and get ready to turn brass into stunning works of art.
Frequently Asked Questions
1.Can You Use Brass On A Lathe?
Brass can indeed be used on a lathe. It is a popular choice due to its durability and attractive finish. However, using proper safety equipment and cutting techniques when working with brass is important, as it can produce sharp chips.
2.Can You Turn Metal On A Wood Lathe?
Turning metal, including brass, on a wood lathe is possible. However, using the right tools and techniques designed for metal turning and proper safety precautions is important. The wood lathe must have enough power, and the cutting tools must be sharp and appropriate for metal turning.
3.Is Brass Easy To Turn?
Brass is generally considered easier to turn than harder metals such as steel. It is softer and more malleable, making it easier to shape. However, brass can be prone to chatter, requiring sharp tools, light cuts, and slower turning speeds for best results. Turning brass can be a rewarding woodworking experience with practice and the right techniques.
4.Can You Turn Copper On A Wood Lathe?
Yes, copper can be turned on a wood lathe. Like brass, copper is a soft metal that is relatively easy to work with. However, it is important to use sharp tools and not overheat the metal. Regularly check for sharp burrs, and smooth the surface with sandpaper or a deburring tool. Always follow safety precautions when turning copper on a wood lathe.
5.What Speed Do You Turn Brass On A Lathe?
The speed at which you turn brass on a lathe can vary depending on the type of brass used and the workpiece’s size. As a general guideline, a spindle speed of around 800-1200 RPM (revolutions per minute) is often recommended for turning brass on a lathe.